Hi Community!
We are pleased to invite you to the upcoming webinar "Machine Learning Toolkit (Python, ObjectScript, Interoperability, Analytics) for InterSystems IRIS" on 26th of March at 10:00 (Moscow time)!
This tag relates to the discussions on the development of analytics and business intelligence solutions, visualization, KPI and other business metrics management.
Hi Community!
We are pleased to invite you to the upcoming webinar "Machine Learning Toolkit (Python, ObjectScript, Interoperability, Analytics) for InterSystems IRIS" on 26th of March at 10:00 (Moscow time)!
I am planning to implement Business Intelligence based on the data in my instances. What is the best way to set up my databases and environment to use DeepSee?

Hi Everyone!
New session recording from Global Summit 2018 is available on InterSystems Developers YouTube Channel:
Hi All,
Can any one know how to change the font style as Italics in Terminal
Running predictive models natively in an InterSystems IRIS Business Process has of course always been the goal of our PMML support, but somehow never made it into the kit because there were a few dependencies and choices that needed addressing and answering. Anyhow, thanks to some pushing and code kindly provided by @Amir Samary (Thanks again Amir!), we finally got it wrapped in a GitHub repo for your enjoyment, review and suggestions.
The following post outlines an architectural design of intermediate complexity for DeepSee. As in the previous example, this implementation includes separate databases for storing the DeepSee cache, DeepSee implementation and settings. This post introduces two new databases: the first to store the globals needed for synchronization, the second to store fact tables and indices.

Hi Community!
Please welcome a new video on InterSystems Developers YouTube Channel:
Alexa: Connect Me with the World of IoT
Hello, I need help in health insight. I am trying to generate reports on deep see but i am not able to pull in the patient ids as these are our requirements for the project. Can anyone help me in unlocking this feature. Can anyone help me with link to correct documentation on how to access the edge gateways of multiple facilities to access the clinical data on sql explorer.
Hi,
How Can I get sentiment analysis (positive or negative attribute) from a source or entity from iKnow REST API?
Hi All!
I asked previously about the DR server in the cloud but actually, I'm curious about the backup server to use as analytics server more than for recovery in DR case.
There is a recommended practice to use an async mirror as a server for BI (InterSystems Analytics, DeepSee)
The question is if I have PRIMARY in the cloud (AWS, Google, Azure, etc) "how far" should async mirror member be placed? Same cloud, same private cloud or it doesn't matter at all for analytics purposes?
Users of analytical applications often need to generate and send out PDF reports comprised of elements of the analytical panel. In the InterSystems stack, this task is solved using the DSW Reports project that is an extension of DeepSeeWeb. In this article, we will explain how to use DSW Reports for generating PDF reports and emailing them.
Hi all. We are going to find duplicates in a dataset using Apache Spark Machine Learning algorithms.
Note: I have done the following on Ubuntu 18.04, Python 3.6.5, Zeppelin 0.8.0, Spark 2.1.1
In previous articles we have done the following:
In this series of articles, we explore Machine Learning and record linkage.
Imagine that we merged databases of neighboring
The following post outlines a more flexible architectural design for DeepSee. As in the previous example, this implementation includes separate databases for storing the DeepSee cache, DeepSee implementation and settings, and synchronization globals. This example introduces one new databases to store the DeepSee indices. We will redefine the global mappings so that the DeepSee indices are not mapped together with the fact and dimension tables.

The row expression defines what dimensions and measures appear on the rows of your pivot table as well as how they appear. Sets and CROSSJOINs are used.
3394731190001
We’re now less than a month away from our annual conference, the InterSystems Global Summit. This year, we’ll be descending on the beautiful outskirts of San Antonio, a city worth visiting for its wonderful river walkway and its 18th century Spanish Mission, even if it hadn’t been the location of this year’s InterSystems event. Leaving the tourist guidance to the tourist guides, let’s take a closer look at what the conference has in stock for you, including a dedicated post-summit symposium on AI and ML on Wednesday October 3!

The source class of a DeepSee cube has a property referencing a different class:
Class ClassA Extends %Persistent {
Property P1 As ClassB;
}When records in class B change, the ^OBJ.DSTIME global for Class A will not be automatically updated. This means that synchronization of cubes based on source class A will not reflect the changes occurred to property P1.
This post will help you determine the best way to achieve synchronization of properties referencing a different class
Hi, Community!
I’m sure you are using Developer Community analytics built with InterSystems Analytics technology DeepSee:
You can find DC analytics n InterSystems->Analytics menu.
DC Analytics shows interactive dashboards on key figures of DC entities: Posts, Comments, and Members.
Since the last week, this analytics project is available for everyone with source code and data on DC Github!
As a developer, usually I'm concerned about how my code health is, and how the other coders code can affect to my own work. And I'm quite sure most of us feel very similar.
In our company we use a Static Code Analysis tool to analyze code for different languages to ensure we are writing high quality and easily maintainable code by following a few best practices in terms of code structure and content. And the question was: why should be different for Caché ObjectScript language?
I was approached recently by and end use who wanted to perform analysis of their databases and see how they could save some space by picking data good for deletion without harming the application. As part of investigation, they wanted to know sizes of globals within datasets. This can be achieved by various means but all of them provide data in text form only.
I thought I might be a good tool for database administrators in general - to see global sizes in a graphical way.
I have a server with rusw locale but in my cube the time dimension shows dates such as "JAN-2018". Is there a way to either localize that (preferably) or just output numbers like "01-2018"?
Architect:
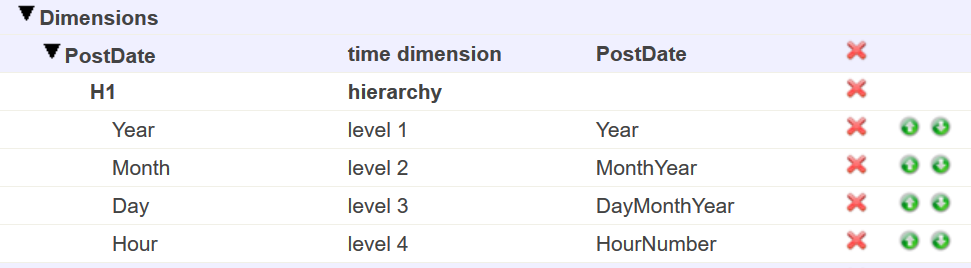
Analyzer:
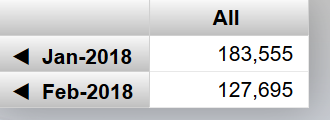
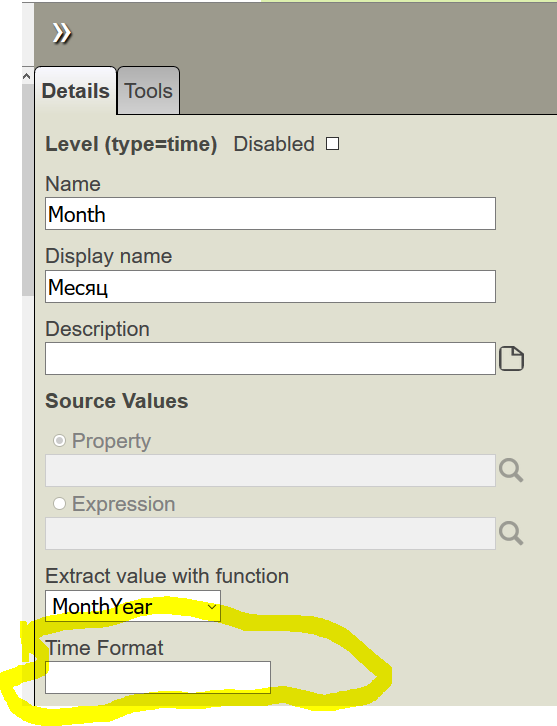
Also in architect, in level settings there is a "Time Format" property, what's that? Tried setting it to 3 but it didn't help.
With the release of InterSystems IRIS, we're also making available a nifty bit of software that allows you to get the best out of your InterSystems IRIS cluster when working with Apache Spark for data processing, machine learning and other data-heavy fun. Let's take a closer look at how we're making your life as a Data Scientist easier, as you're probably already facing tough big data challenges already, just from the influx of job offers in your inbox!
The following post concludes the series with a list of all databases seen in the example for the fully flexible architecture.

The following post is a guide to implement a basic architecture for DeepSee. This implementation includes a database for the DeepSee cache and a database for the DeepSee implementation and settings.

Hi Everyone!
New session recording from Global Summit 2017 is already on InterSystems Developers YouTube:
Predicting Your Manhattan Cab Ride Fare
Hi, Community!
This is the 3rd part of DeepSee Web story - Angular base UI for DeepSee Dashboards, see the beginning here.
By design, DSW provides an implementation for every widget in DeepSee library. But there are some extra features in DSW which make solutions built with DSW dashboards more functional. This article describes it.
Last week, we announced the InterSystems IRIS Data Platform, our new and comprehensive platform for all your data endeavours, whether transactional, analytics or both. We've included many of the features our customers know and loved from Caché and Ensemble, but in this article we'll shed a little more light on one of the new capabilities of the platform: SQL Sharding, a powerful new feature in our scalability story.
Hi, Community!
In the second part about DeepSee Web, I’ll describe what customization options you have with DSW.
There are two types of customizations: widget customization and dashboard panel customization.
Example of dashboard customization on Developer Community analytics.
Learning Services Live Webinars are back!
At this year’s Global Summit, InterSystems debuted InterSystems IRIS Data Platform™, a single, comprehensive product that provides capabilities spanning data management, interoperability, transaction processing, and analytics. InterSystems IRIS sets a new level of performance for the rapid development and deployment of data-rich and mission-critical applications. Now is your chance to learn more!
Joe Lichtenberg, Director of Product and Industry Marketing for InterSystems, presents "Introducing InterSystems IRIS Data Platform", a high-level
Hi guys,
I'm trying to immigrate some of my HealthInsight dashboards and pivot tables to another HS instance.
In some pivot tables, I defined them with a set of calculated dimensions defined in the analyzer, e.g as below:
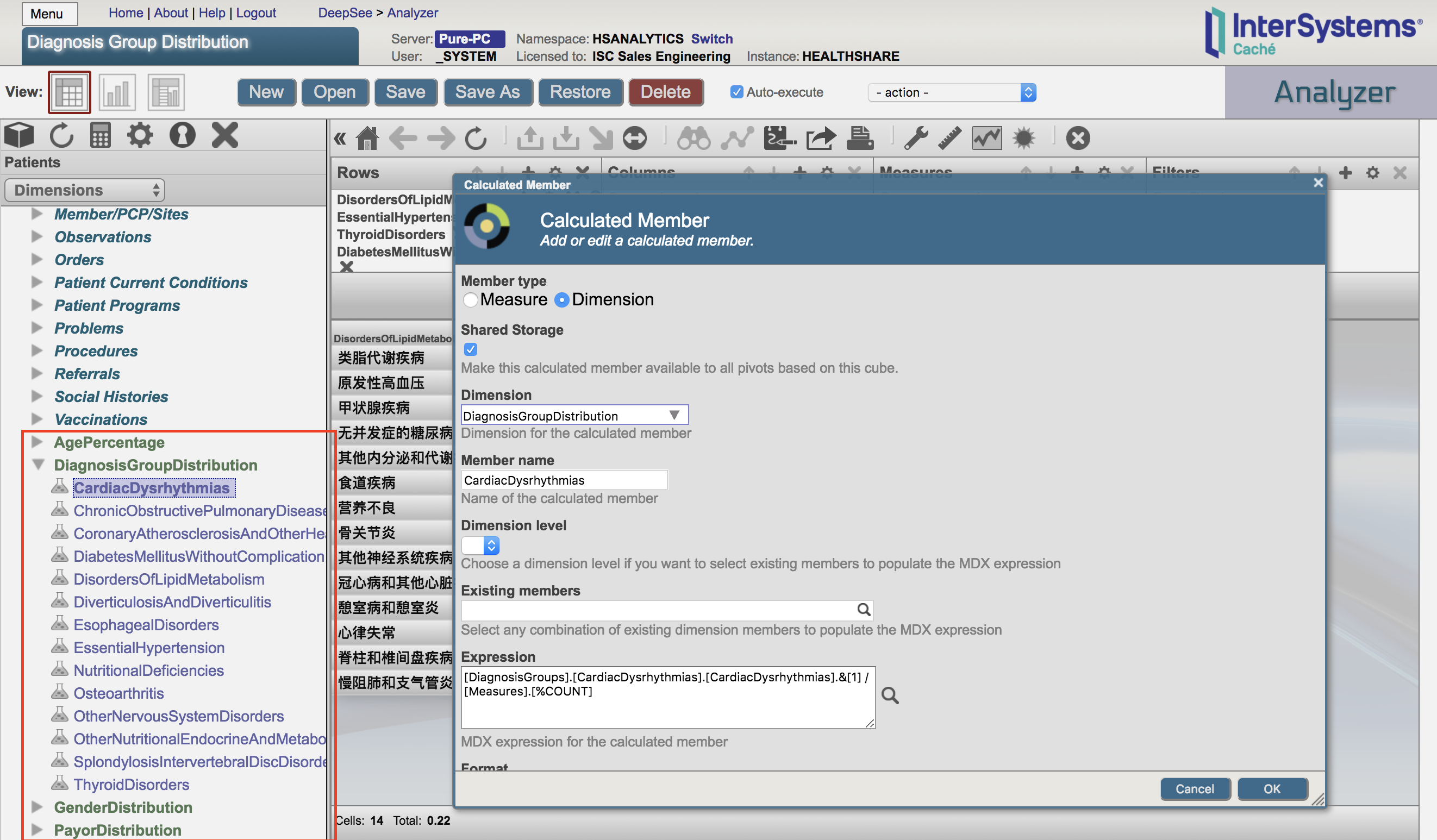
Then when I exported the cubes and pivot tables in used to my new envirmonment. When I open my pivot tables again, the calculated dimensions are missing and hence my pivot tables no longer work:
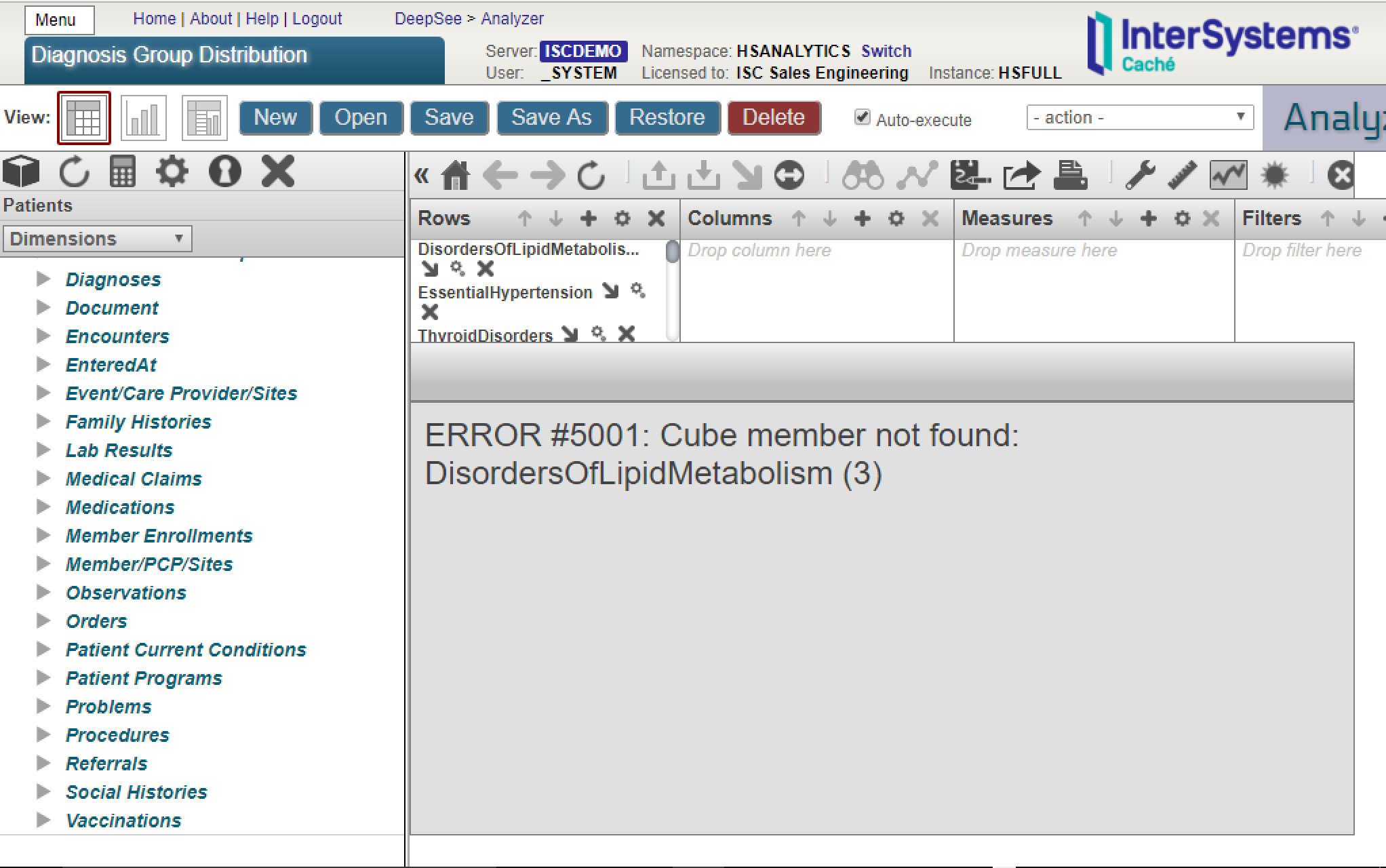
Is there any way to export those calculated dimensions so that I can used them else where?
Apache Spark has rapidly become one of the most exciting technologies for big data analytics and machine learning.Spark is a general data processing engine created for use in clustered computing environments.Its heart is the Resilient Distributed Dataset (RDD) which represents a distributed, fault tolerant, collection of data that can be operated on in parallel across the nodes of a cluster.Spark is implemented using a combination of Java and Scala and so comes as a library that can run on any JVM.