Overview
Encryption of sensitive data becomes more and more important for applications. For example patient names, SSN, address-data or credit card-numbers etc..
Cache supports different flavors of encryption. Block-level database encryption and data-element encryption. The block-level database encryption protects an entire database. The decryption/encryption is done when a block is written/read to or from the database and has very little impact on the performance.
With data-element encryption only certain data-fields are encrypted. Fields that contain sensitive data like patient data or credit-card numbers. Data-element encryption is also useful if a re-encryption is required periodically. With data-element encryption it is the responsibility of the application to encrypt/decrypt the data.
Both encryption methods leverage the managed key encryption infrastructure of Caché.
The following article describes a sample use-case where data-element encryption is used to encrypt person data.
But what if you have hundreds of thousands of records with an encrypted datafield and you have the need to search that field? Decryption of the field-values prior to the search is not an option. What about indices?
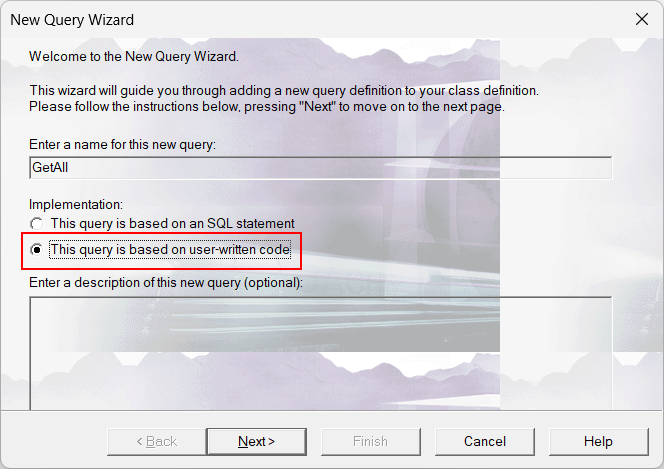
This article describes a possible solution and develops step-by-step a small example how you can use SQL and indices to search encrypted fields.

.png)