Hello all,
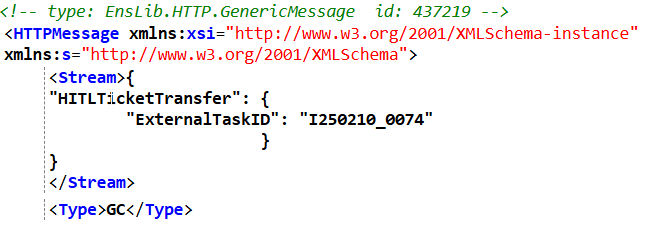
I have a EnsLib.HTTP.GenericMessage inbound from a webhook with a GC stream.
My router is defined as the following:
General Message Routing Rule
The msgClass for said rule is: EnsLib.HTTP.GenericMessage
I have tried a few variants of using a Contains in the condition to check the following: Document.StreamGC.Attributes.
I want to check the Stream for "HITL". If it contains that, we send downstream.
Is there a way to do this within the condition in the rule?
Is the best solution to instead write a function that rewinds the stream and returns a flag?
Thank you!



(1).jpg)




