In this article I'll show you how to set up in your laptop, very quickly, a cluster of IRIS nodes in sharding. It's not the goal of this article neither to talk about sharding in detail nor define a deployment of a production ready architecture, but to show how to set up quickly, in your own machine, a cluster of IRIS instances configured as shard nodes, with which you'll able to play and test this functionality. If you're insterested in knowing more about sharding in IRIS, take a look at the documentation clicking here.
First and foremost, I want to remark that IRIS sharding will allow us 2 things:
- Define, load and query shard tables, which data will be distributed transparently between the cluster's nodes
- Define federated tables, which offer a global and composed view of data belonging to different tables that will be physically stored in different distributed nodes
So, as I said, we let for other article playing with shard or federated tables, and just focus now in the previous step, that is, setting up the cluster of shard nodes.
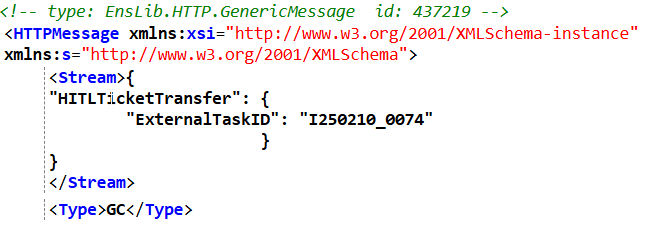



(1).jpg)




