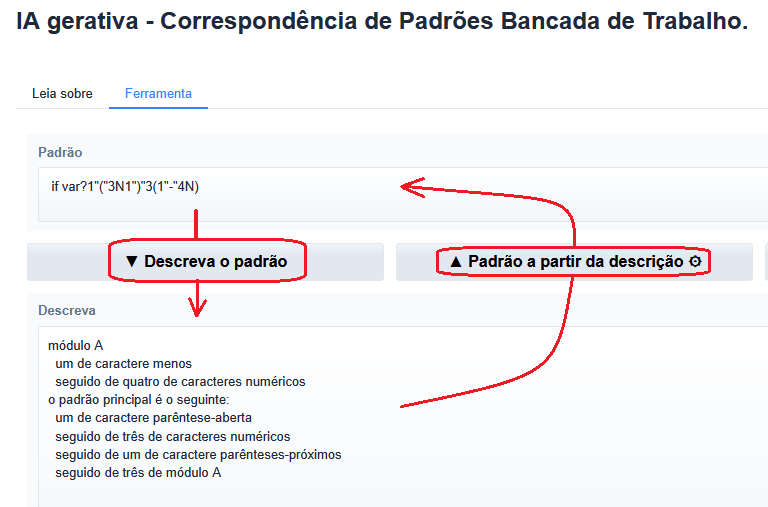
Dear community, I have a confession to make. I have not gotten over Zen yet. Alas, all good things must come to an EOF, so I am currently learning about Angular. I am working on proving to myself that with the right back end and Angular components, I can deliver to myself and my team a very Zen-like experience in this environment.


.png)