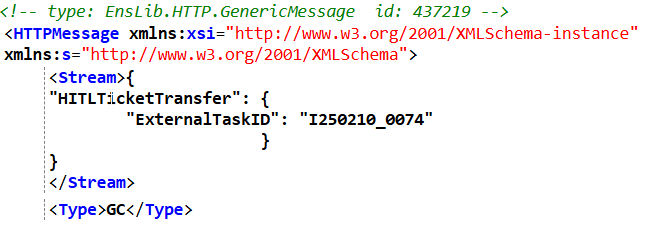
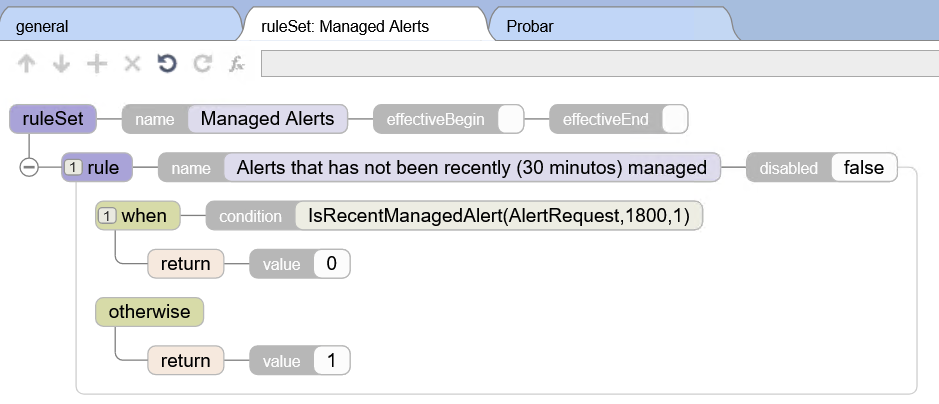
I may have mentioned this before: I believe the Visual Traces, these sequence diagrams with full content of each step, are a fantastic feature of the IRIS Data platform! Detailed information about how the API works internally, as a visual trace, can be very useful for projects on the IRIS platform. Of course, this applies when we are not developing a high-load solution, in which case we simply don't have time for saving/reading messages. For all other cases, welcome to this tutorial!
Dev Community resources
Events
27-30 Apr
Trending posts
[Sweepstakes] Suggest topics for our next free hands-on tutorials!
by Irène Mykhailova
ObjectScript Search — Full-Text Server-Side Search for VS Code, Right Now
by Guillaume Rongier
Vector Search with Embedded Python in InterSystems IRIS
by Alyssa Ross
Show more (2)
Trending apps
MDX2JSON
by Eduard Lebedyuk
47478
Embedded Git
by Pravin Barton
9719
Intersystems-Monitoring
by Teunis Stolker
14731
Featured app
iris-airflow-provider
by Muhammad Waseem
News
Community in numbers
Members
26.3K
Posts
25.7K
Comments
60K
Views
13.4M
Likes
37.4K



(1).jpg)




