Introduction
Database performance has become a critical success factor in a modern application environment. Therefore identifying and optimizing the most resource-intensive SQL queries is essential for guaranteeing a smooth user experience and maintaining application stability.
This article will explore a quick approach to analyzing SQL query execution statistics on an InterSystems IRIS instance to identify areas for optimization within a macro-application.
Rather than focusing on real-time monitoring, we will set up a system that collects and analyzes statistics pre-calculated by IRIS once an hour. This approach, while not enabling instantaneous monitoring, offers an excellent compromise between the wealth of data available and the simplicity of implementation.
We will use Grafana for data visualization and analysis, InfluxDB for time series storage, and Telegraf for metrics collection. These tools, recognized for their power and flexibility, will allow us to obtain a clear and exploitable view.
More specifically, we will detail the configuration of Telegraf to retrieve statistics. We will also set up the integration with InfluxDB for data storage and analysis, and create customized dashboards in Grafana. This will help us quickly identify queries requiring special attention.
To facilitate the orchestration and deployment of these various components, we will employ Docker.

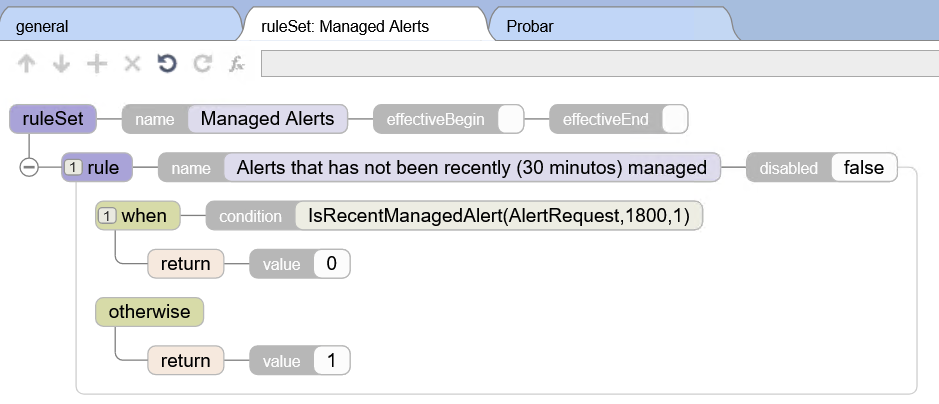
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)