Hello IRIS community,
InterSystems Certification is developing a certification exam for InterSystems IRIS Developer professionals, and if you match the exam candidate description given below, we would like you to beta test the exam. The exam will be available for beta testing on March 5, 2025, and the beta testing must be completed by April 20, 2025.
What are my responsibilities as a beta tester?
You must schedule and take the exam by April 20, 2025. The exam will be administered in an online proctored environment free of charge (the standard fee of $150 per exam is waived for all beta testers). The InterSystems Certification team will then perform a careful statistical analysis of all beta test data to set a passing score for the exam. The analysis of the beta test results will take 6-8 weeks, and once the passing score is established, you will receive an email notification from InterSystems Certification informing you of the results. If your score on the exam is at or above the passing score, you will have earned the certification!
Note: Beta test scores are completely confidential.
Interested in participating? Read the Exam Details and Instructions below:
Exam Details
Exam title: InterSystems IRIS Developer Professional
Candidate description: A back-end software developer who:
- writes and executes efficient, scalable, maintainable, and secure code on (or adjacent to) InterSystems IRIS using best practices for the development life cycle,
- effectively communicates development needs to systems and operations teams (e.g., database architecture strategy),
- integrates InterSystems IRIS with modern development practices and patterns, and
- is familiar with the different data models and modes of access for InterSystems IRIS (ObjectScript, Python, SQL, JDBC/ODBC, REST, language gateways, etc.)
Number of questions: 62
Time allotted to take exam: 2 hours
Recommended preparation: Review the content below before taking the exam.
Classroom Training
- Developing with InterSystems Objects and SQL (classroom, 5 days)
Online Learning:
- Getting Started with InterSystems IRIS for Coders (program, 20h 30m)
- Using SQL in InterSystems IRIS (learning path, 3h 45m)
- Managing InterSystems IRIS for Developers (learning path, 2h 30m)
- Analyzing Data with InterSystems IRIS BI (learning path, varies)
- Deploying and Testing InterSystems Products Using CI/CD Pipelines (course, 25m)
Recommended practical experience: At least 2 years of experience developing with InterSystems IRIS and a basic understanding of ObjectScript is recommended.
Exam practice questions
A set of practice questions is provided here to help familiarize candidates with question formats and approaches.
Exam format
The questions are presented in two formats: multiple choice and multiple response. Access to InterSystems IRIS Documentation will be available during the exam.
DISCLAIMER: Please note this exam has a 2-hour time limit. While InterSystems documentation will be available during the exam, candidates will not have time to search the documentation for every question. Thus, completing the recommended preparation before taking the exam, and searching the documentation only when absolutely necessary during the exam, are both strongly encouraged!
System requirements for beta testing
- Working camera & microphone
- Dual-core CPU
- At least 2 GB available of RAM memory
- At least 500 MB of available disk space
- Minimum internet speed:
- Download - 500kb/s
- Upload - 500kb/s
Exam topics and content
The exam contains questions that cover the areas for the stated role as shown in the exam topics chart immediately below. All questions are based on InterSystems IRIS v2024.1+.
|
Topic |
Subtopic |
Knowledge, skills, and abilities |
| 1. Best practices: Architecture | 1.1 Determines database storage strategy in InterSystems IRIS |
|
| 1.2. Determines data structures |
|
|
| 1.3. Plans data lifecycle |
|
|
| 2. Best practices: Development lifecycle | 2.1 Uses recommended development tools and workflows with InterSystems IRIS |
|
| 2.2 Integrates InterSystems IRIS with CI/CD pipelines |
|
|
| 2.3 Uses source control with InterSystems IRIS |
|
|
| 3. Best practices: Data retrieval | 3.1 Uses Python with InterSystems IRIS |
|
| 3.2 Connects to InterSystems IRIS |
|
|
| 3.3. Uses SQL with InterSystems IRIS |
|
|
| 3.4 Creates REST services |
|
|
| 4. Best practices: Code | 4.1 Writes defensive code |
|
| 4.2 Writes secure code |
|
|
| 4.3 Ensures data integrity |
|
|
| 4.4 Implements concurrency controls |
|
Instructions:
Please review the following instructions for scheduling and buying an exam:
- From our exam store, log in with your InterSystems Single Sign-On (SSO) account.
- If necessary, please register for an account.
- Select InterSystems IRIS Developer Professional - Beta and click Get Started.
- Verify system compatibility as instructed. The Safe Exam Browser download requires administrative privileges on your device.
- Run the setup test to ensure the device satisfies the exam requirements.
- Schedule your exam – this must be done before checking out. The exam must be taken at least 24 hours after, but within 30 days, of scheduling the exam.
- Review the InterSystems Certification Program Agreement.
- Confirm your appointment. You will receive an email from Certiverse with your exam appointment details.
- You can access your reservations and history through the Exam Dashboard available through the MY EXAMS menu.
Below are important considerations that we recommend to optimize your testing experience:
- Read the Taking InterSystems Exams and Exam FAQs pages to learn about the test-taking experience.
- Read the InterSystems Certification Exam Policies.
- On the day of your exam, log in to Certiverse at least 10 minutes before your scheduled time, launch the exam under MY EXAMS, and wait for the proctor to connect.
- Please have your valid government ID ready for identification. The proctor will walk you through the process of securing your room and releasing the exam to you.
You may cancel or reschedule your appointment without penalty as long as the action is taken at least 24 hours in advance of your appointment. The voucher code will reactivate and you can use it to reschedule the exam.
Please contact certification@intersystems.com if you have any questions or need assistance, and we encourage you to share any feedback about the exam, whether positive or negative.

 Olá!
Olá!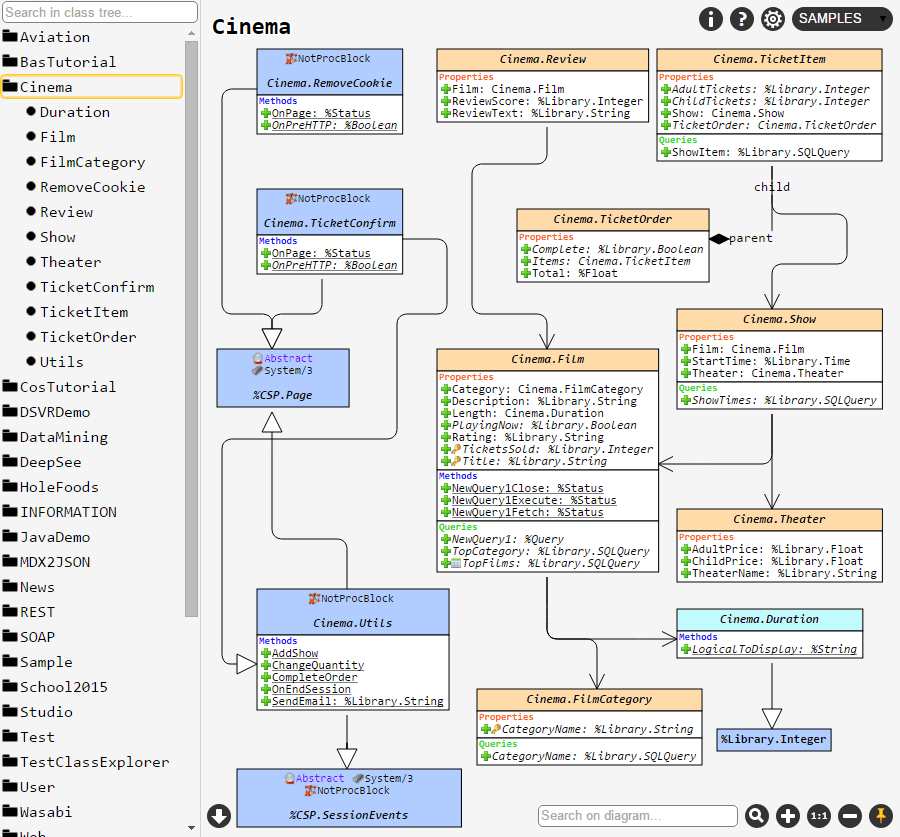
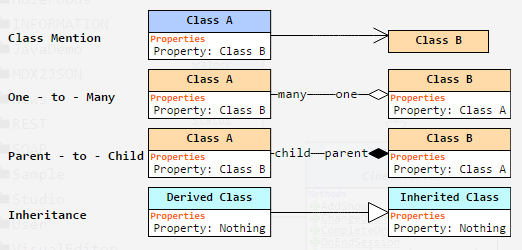
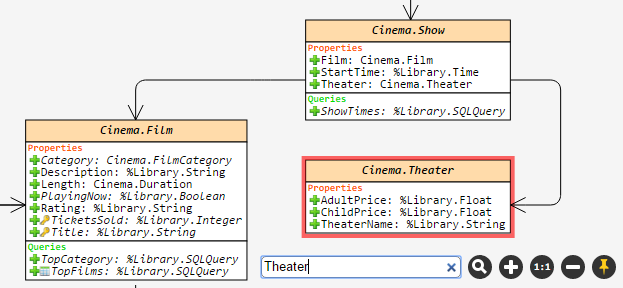

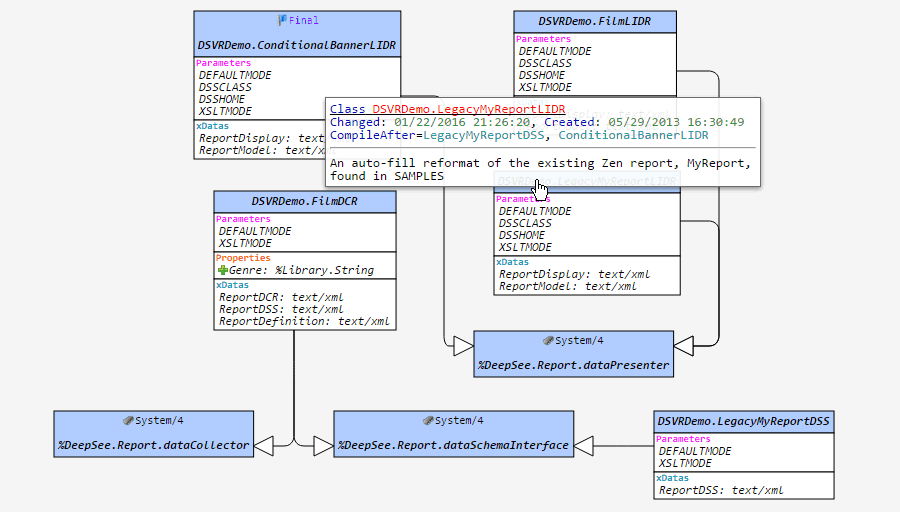
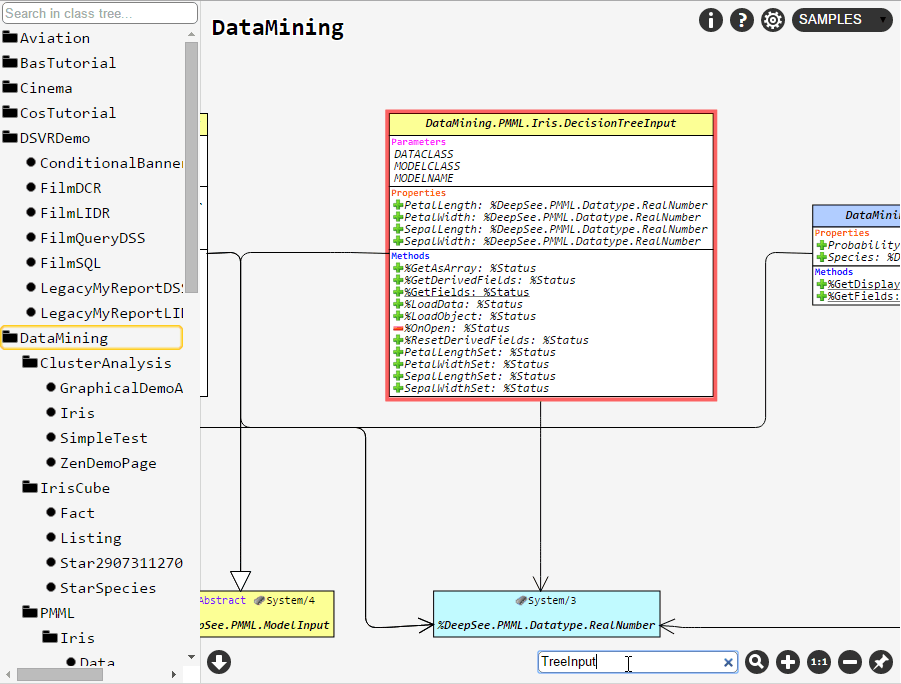
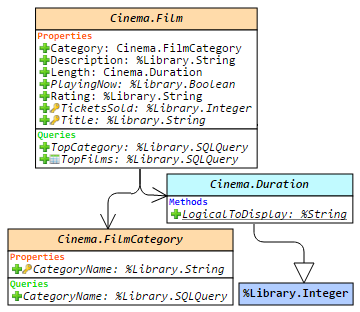
 , a posição dos elementos no diagrama do conjunto atual de classes (ou um pacote) será salva. Por exemplo, se você selecionar as classes A e B e, em seguida, salvar a visualização com o botão de alfinete, você verá exatamente a mesma visualização ao escolher as classes A e B novamente, mesmo após reiniciar o navegador ou a máquina. Mas se você escolher apenas a classe A, o layout será o padrão.
, a posição dos elementos no diagrama do conjunto atual de classes (ou um pacote) será salva. Por exemplo, se você selecionar as classes A e B e, em seguida, salvar a visualização com o botão de alfinete, você verá exatamente a mesma visualização ao escolher as classes A e B novamente, mesmo após reiniciar o navegador ou a máquina. Mas se você escolher apenas a classe A, o layout será o padrão.