10:47 AM — Jose Garcia's creatinine test results arrive at the hospital FHIR server.
2.1 mg/dL — a 35% increase from last month.
What happens next?
- Most systems: ❌ The result sits in a queue until a clinician reviews it manually — hours or days later.
- This system: 👍 An AI agent evaluates the trend, consults clinical guidelines, and generates evidence-based recommendations — in seconds, automatically.
No chatbot. No manual prompts. No black-box reasoning.
This is event-driven clinical decision support with full explainability:
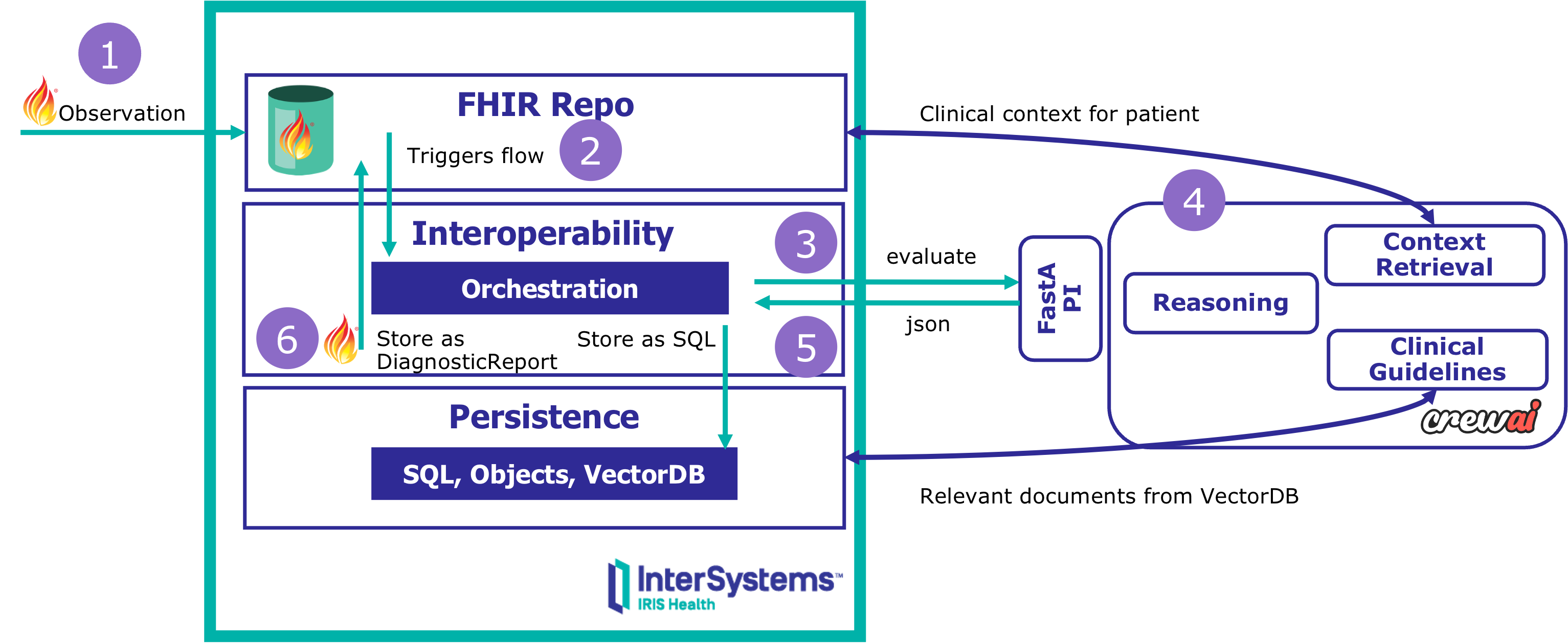
✅ Triggered automatically by FHIR events
✅ Multi-agent reasoning (context, guidelines, recommendations)
✅ Complete audit trail in SQL (every decision, every evidence source)
✅ FHIR-native outputs (DiagnosticReport published to server)
Built with:
- InterSystems IRIS for Health — Orchestration, FHIR, persistence, vector search
- CrewAI — Multi-agent framework for structured reasoning
You'll learn: 🖋️ How to orchestrate agentic AI workflows within production-grade interoperability systems — and why explainability matters more than accuracy alone.
.png)

