Using Machine Learning to Organize the Community - 1
This is my introduction to a series of posts explaining how to create an end-to-end Machine Learning system.
Starting with one problem
Our IRIS Development Community has several posts without tags or wrong tagged. As the posts keep growing the organization of each tag and the experience of any community member browsing the subjects tends to decrease.
First solutions in mind
We can think some usual solutions for this scenario, like:
- Take a volunteer to read all posts and fix the mistakes.
- Pay a company to fix all mistakes.
- Send an email to each post writer to review the texts from past.
My Solution
What if we could teach a machine to do this job?
 We have a lot of examples on cartoons, anime or movies to remember what can be wrong by teaching a machine...
We have a lot of examples on cartoons, anime or movies to remember what can be wrong by teaching a machine...
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a very broad topic and I will do my best to explain my vision of the topic. Backing to the problem that we still need to solve: If we take look at the usual solutions all of then consider interpretation of a text. And how can we teach a machine to read a text, understand the correlation of the text with a tag? First we need to explore the data and take some insights about it.
Classification? Regression?
When you start to study Machine Learning both of these above therms are always used. But how to know what do you need to go deep?
-Classification: A classification machine learning algorithm predicts discrete values.
-Regression: A regression machine learning algorithm predicts continuous values.
Looking at our problem we need to predict discrete values (all tags exists)
It's all about data!
All posts data was provided here.
Post
SELECT
id, Name, Tags, Text
FROM Community.Post
Where
not text is null
order by id
| id | Name | Tags | Text |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1946 | Introduction to Web Services | Web Development,Web Services | This video is an introduction to web services. It explains what web services are, their usage, and how to administer them. Web Services are also known as "SOAP". This session includes information on security and security policy. |
| 1951 | Tools for Caché | Caché | This Tech Tip reviews various tools available from the Caché in the Windows System Tray. You will see how to access the Studio IDE, Terminal, the System Management Portal, SQL, Globals, Documentation, Class Reference, and Remote System Access. |
| 1956 | Getting Started with Caché | Caché | Getting Started with Caché will introduce Caché and its architecture. We will also look at the development tools, documentation and samples available. |
Tags
| ID | Description |
|---|---|
| .NET | NET Framework (pronounced dot net) is a software framework developed by Microsoft that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. Official site. .NET support in InterSystems Data Platform. |
| .NET Experience | InterSystems .NET Experience reveals the options of interoperability between .NET and InterSystems IRIS Data Platform. See more details here. .NET official site |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. These processes include learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions) and self-correction. Learn more. |
| API | Application Programming Interface (API) is a set of subroutine definitions, protocols, and tools for building application software. In general terms, it is a set of clearly defined methods of communication between various software components. Learn more. |
Now we know how the data looks like. But know the data design isn't enough to create a Machine Learning Model.
What is a Machine Learning Model?
A machine learning model is a combination of a Machine Learning Algorithm with Data. After combining a technique with data a model can start predicting.
Accuracy
If you think that ML Models never make mistakes you should understand better the model accuracy. I few words accuracy is how the model perform in predictions. Usually accuracy is expressed in percent like numbers. So someone say "I had created a model with 70% accuracy". This means that for 70% of predictions, the model will predict correctly. The other 30% will go with the wrong prediction.
NLP - Natural Language Processing
NLP is a field of Machine Learning that works with the ability of a computer to understand and analyse human language. And yes our problem can be solved with NLP.
Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Most of Machine Learning Algorithms has one thing in common: they use as input NUMBERS. Yes I know... this was the most difficult to understand how to create Machine Learning models.
If all the posts and tags are text how does the model could work?
Good part of the work in a ML Solution is transform the data into something that can be used in a algorithm. This work is called Feature Engineering. In this case is more complicated because the data are unstructured. But a short explantion is* I transformed each word of text in a unique id represented by a number. SKLearn and other python libs should help you to do this in a easy way.
Demonstration
I have deployed the trained model as a demo here: http://iris-ml-suite.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com/
What's next?
In next post I'll show the code and ways to do all the modeling. Don't miss!
If this article help you or you like the content vote:
This application is at the current contest on open exchange, you can vote in https://openexchange.intersystems.com/contest/current in my application iris-ml-suite
Comments
Renato, this is impressive!
Is it possible to give an URL of the post to your solution and get the tags list back?
E.g. for this post?
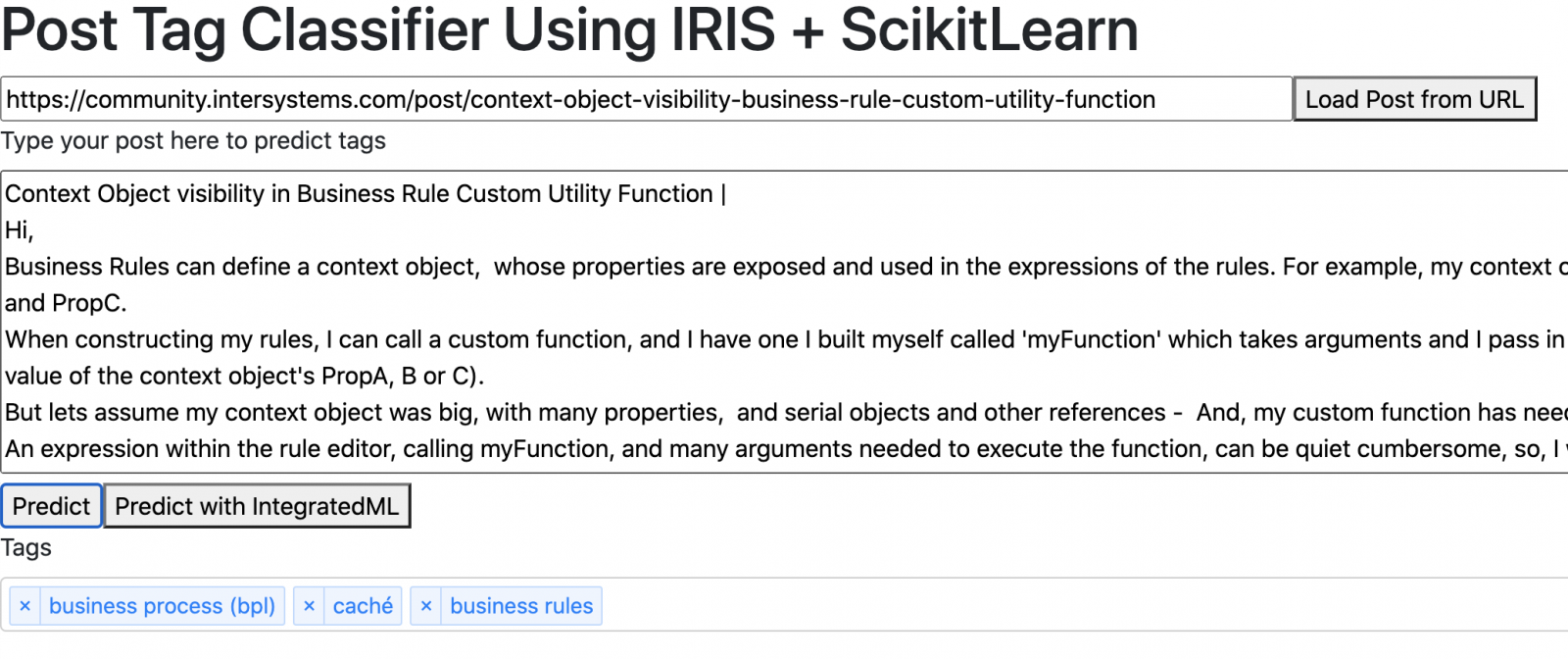
Sure! And I can perform over all registers too...
Magically now you can load the post by url. In a short future I can provide as api to community or using python gateway attach to community server!
Works like a charm!
IntegratedML button didn't work for me - not implemented yet?
Great!
Later I’ll check what happened to integratedml button.
Renato! Do you plan to provide an API?
URL or text as input, tags as output?
Hi Renato!
E.g. here the author has introduced absolutely random tags (Database, Developer Community).
The proper tags could be: Caché, SQL
Is there a way to help the system to educate itself with proper tag sets?
If I understand well. Yes there is some solutions with my ML Model. We can call my model to sugest the tags, and the author can change which I think is the more effective. Is this? To serve my model I can serve it in python or use the IntegratedML to the other one so just choose the best model and use.
Yes, I think of using it with the site. We may introduce it as an option for authors to use "guessed" tags, or to moderators to update it. Curious to see the IntegratedML option working too!
Hi Renato!
A small note:
SELECT id, Name, Tags, Text FROM Community.Post Where not text is null order by idSELECT id, Name, Tags, Text FROM Community.Post Where not text is null order by idDo we really have posts without text there?
Yes we do. I have observed this when I was modeling in python sklearn. So I decided to ignore those. Here querys comparing counts of register with nulls and without nulls:
7631 (including nulls)
7504 (excluding nulls)
|
SELECT count(id) FROM Community.Post order by id |
Namespace: PYTHON
Result #1
| Aggregate_1 |
|---|
| 7631 |
1 row(s) affected
2020-07-20 01:48:27 Routine: %sqlcq.PYTHON.cls264
|
Result #1
| Aggregate_1 |
|---|
| 7504 |
1 row(s) affected