Facial Recognition with InterSystems Vector Search and DeepFace
The facial recognition has become the most popular method for validating people's identities, thus enabling access to systems, confirmation of personal and documentary data, and approval of actions and documents.
The challenges are related to performance when the database is very large, accuracy, and especially the privacy of biometric facial data. For these challenges, nothing is better than using InterSystems Vector Search, as it allows:
- Performing vector searches in millions of records with much faster responses than traditional methods.
- The vector and mathematical models used by Vector Search have high accuracy without sacrificing performance.
- It is not necessary to store the images of the faces, but only the image embeddings, making reverse engineering impossible. This allows full compliance with GDPR, LGPD, and other personal data privacy regulations.
This article details the step-by-step process of collecting, processing, storing, and performing vector face searches. Deepface, a very popular Python library for processing human faces and transforming them into embeddings, is used, along with InterSystems IRIS Vector Search to perform vector comparisons on the stored embeddings, enabling facial recognition in near real-time.
Installation and use of the solution
Follow these steps to install face-recognition (an open-source solution based on Deepface and IRIS):
-
Clone/git pull the repo into any local directory
$ git clone https://github.com/yurimarx/facial-matching.git $ cd facial-matching $ docker-compose build $ docker-compose up -dNote: the docker-compose build step it's time-consuming because the deepface models are downloaded at this stage.
- Open the App http://localhost:8501.
-
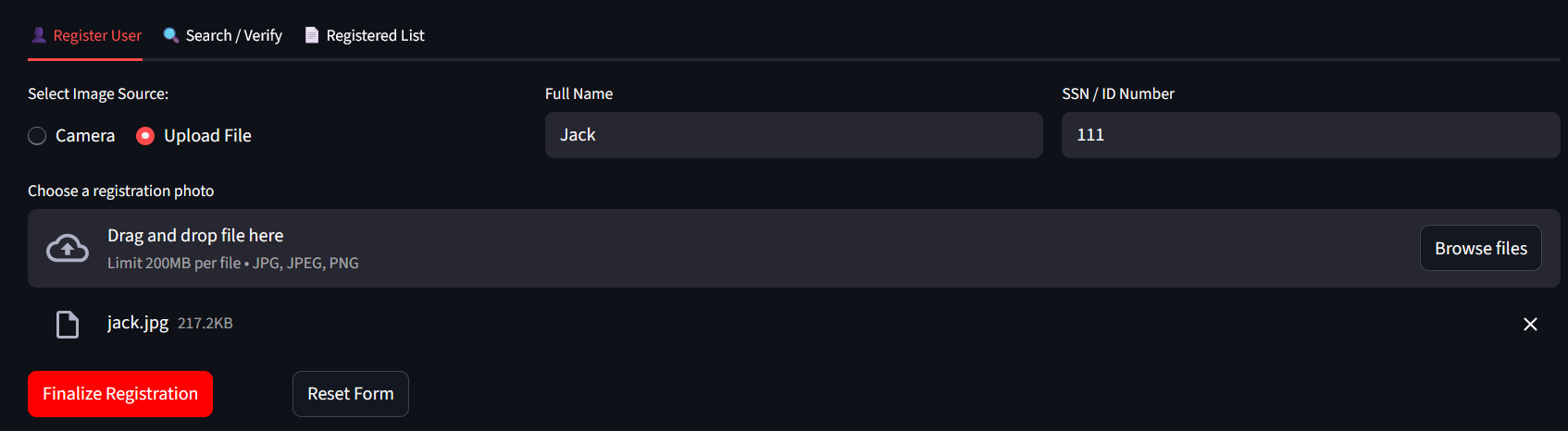
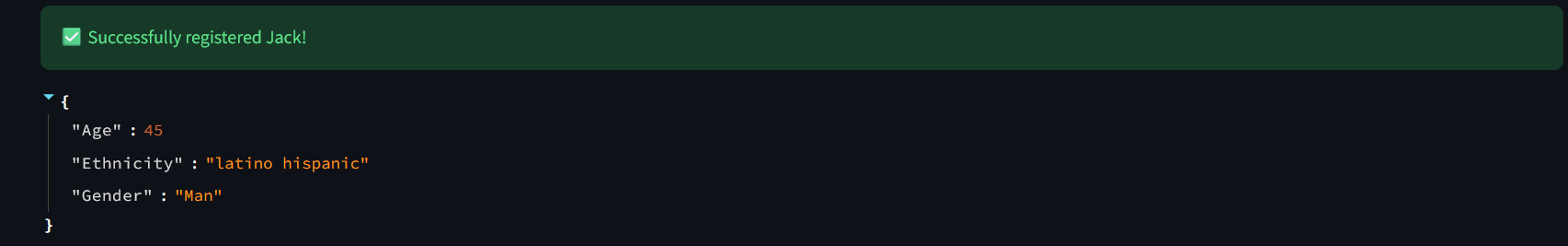
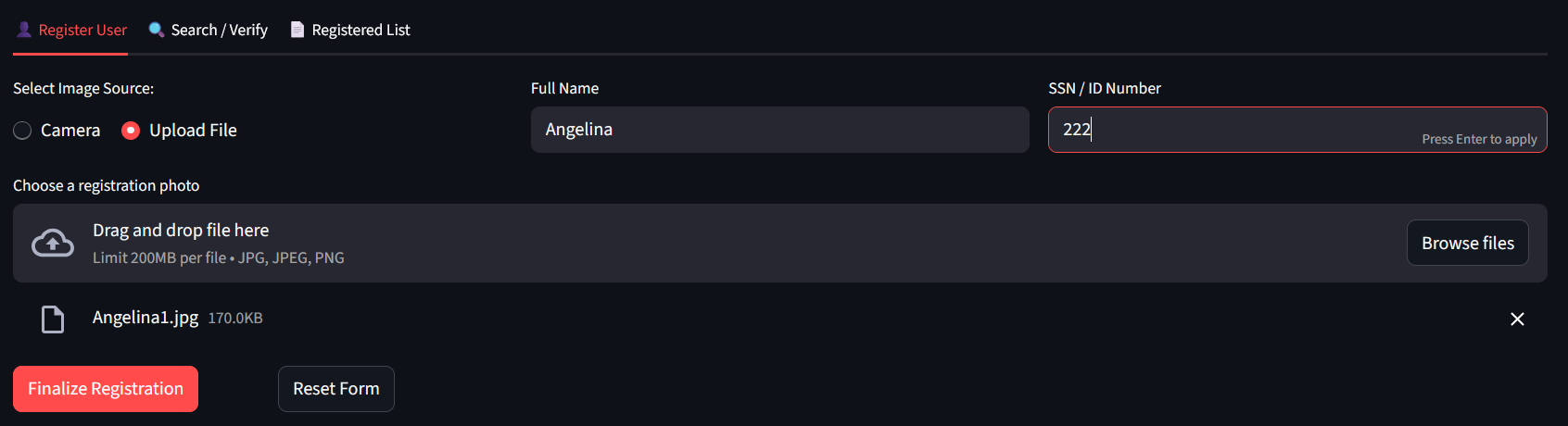
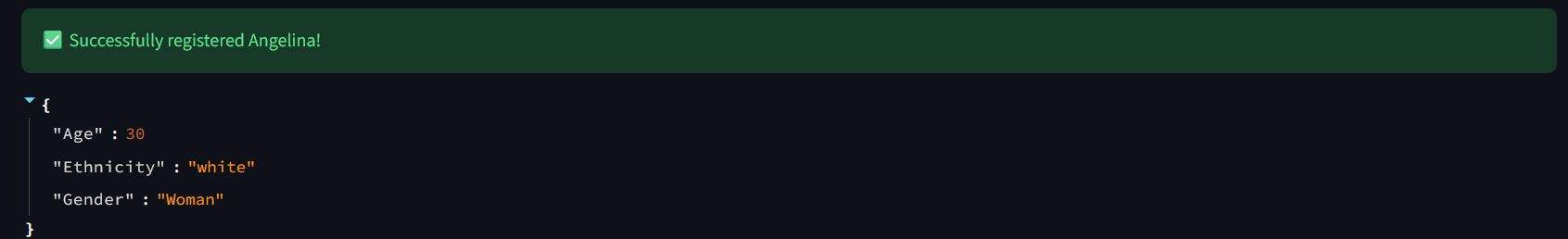
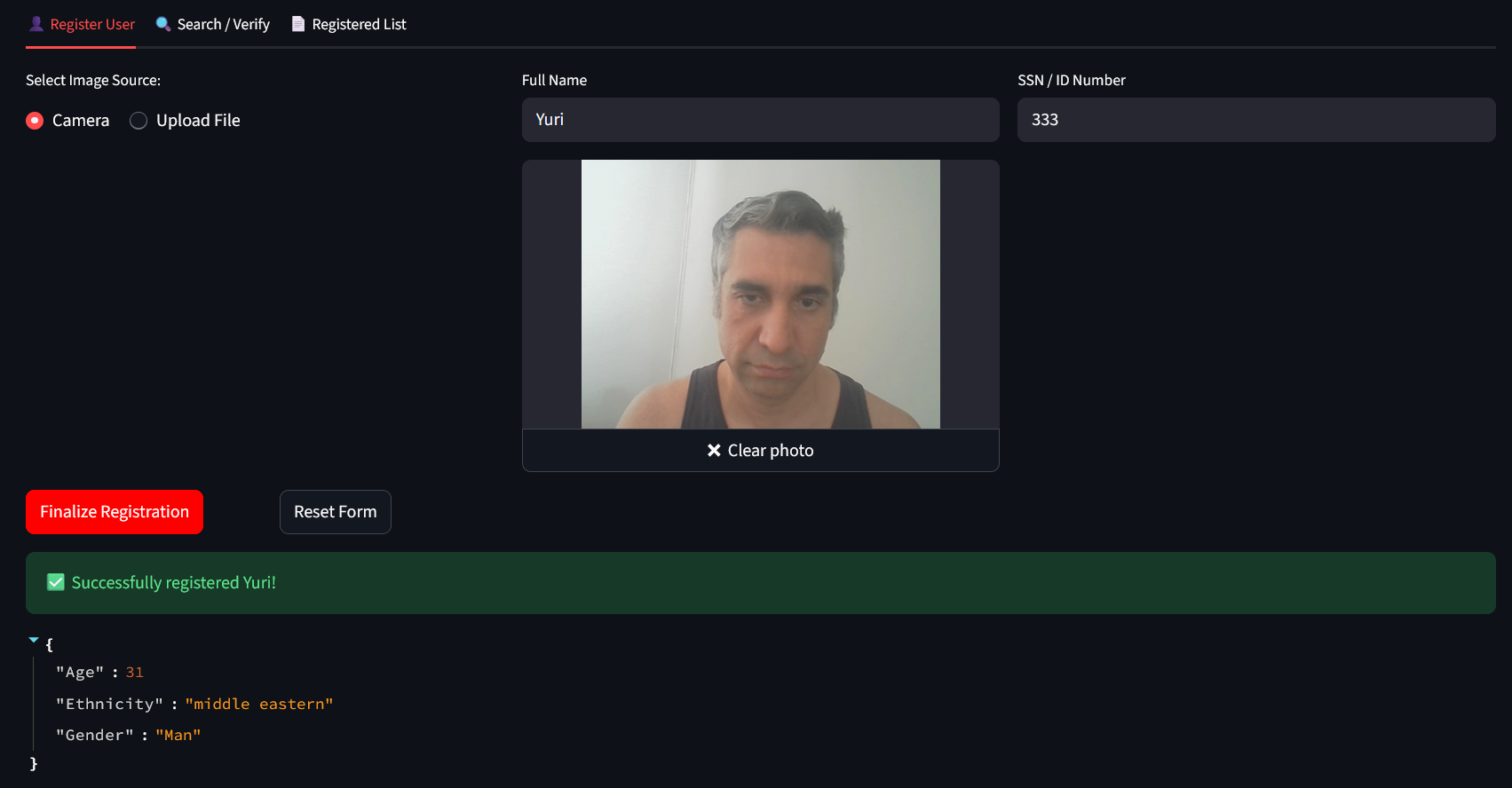
Register some persons (select Camera and Take Photo to capture your image with your PC Camera or upload files. Click Finalize Registration to save person into IRIS DB and Reset form to clear the form and use it again):
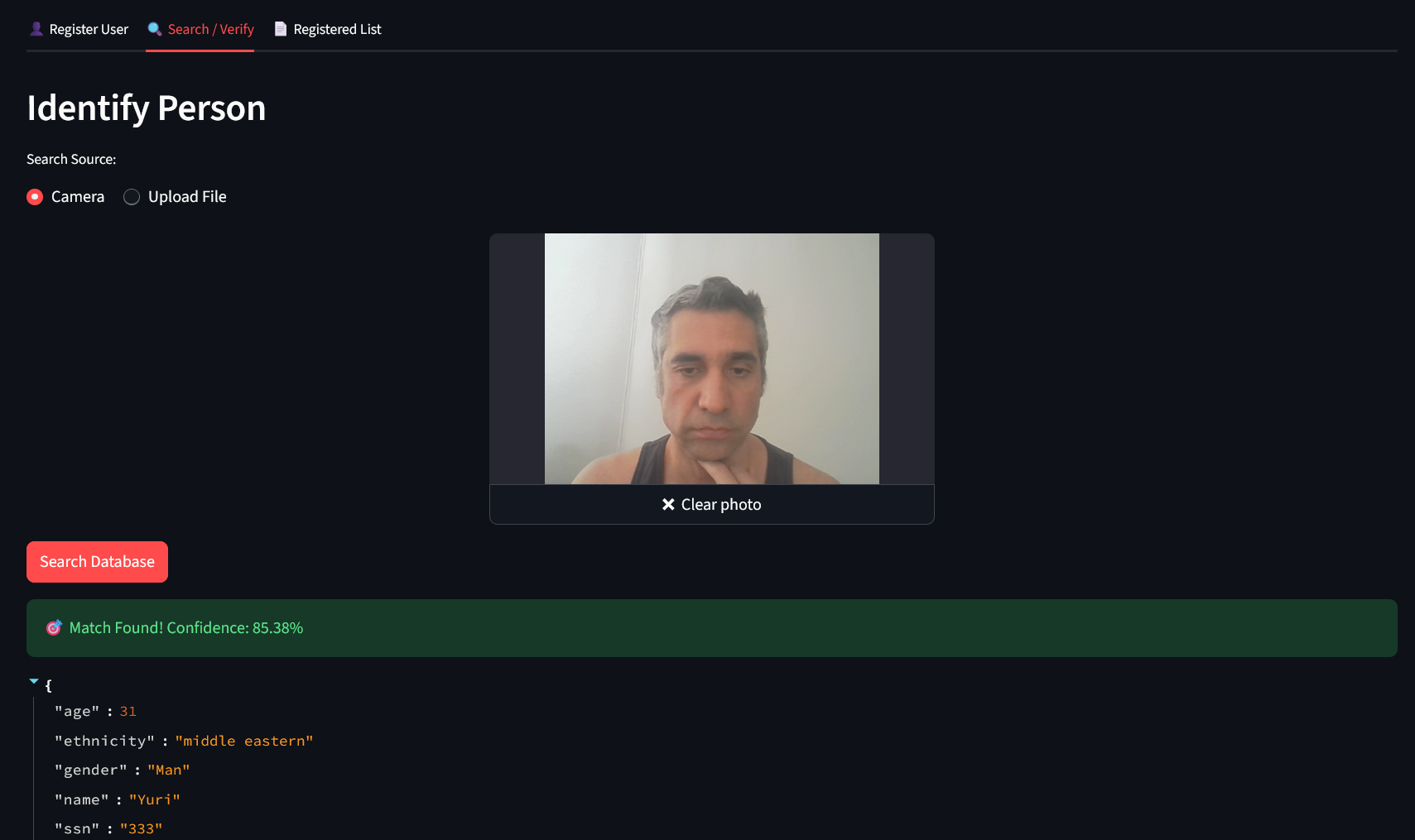
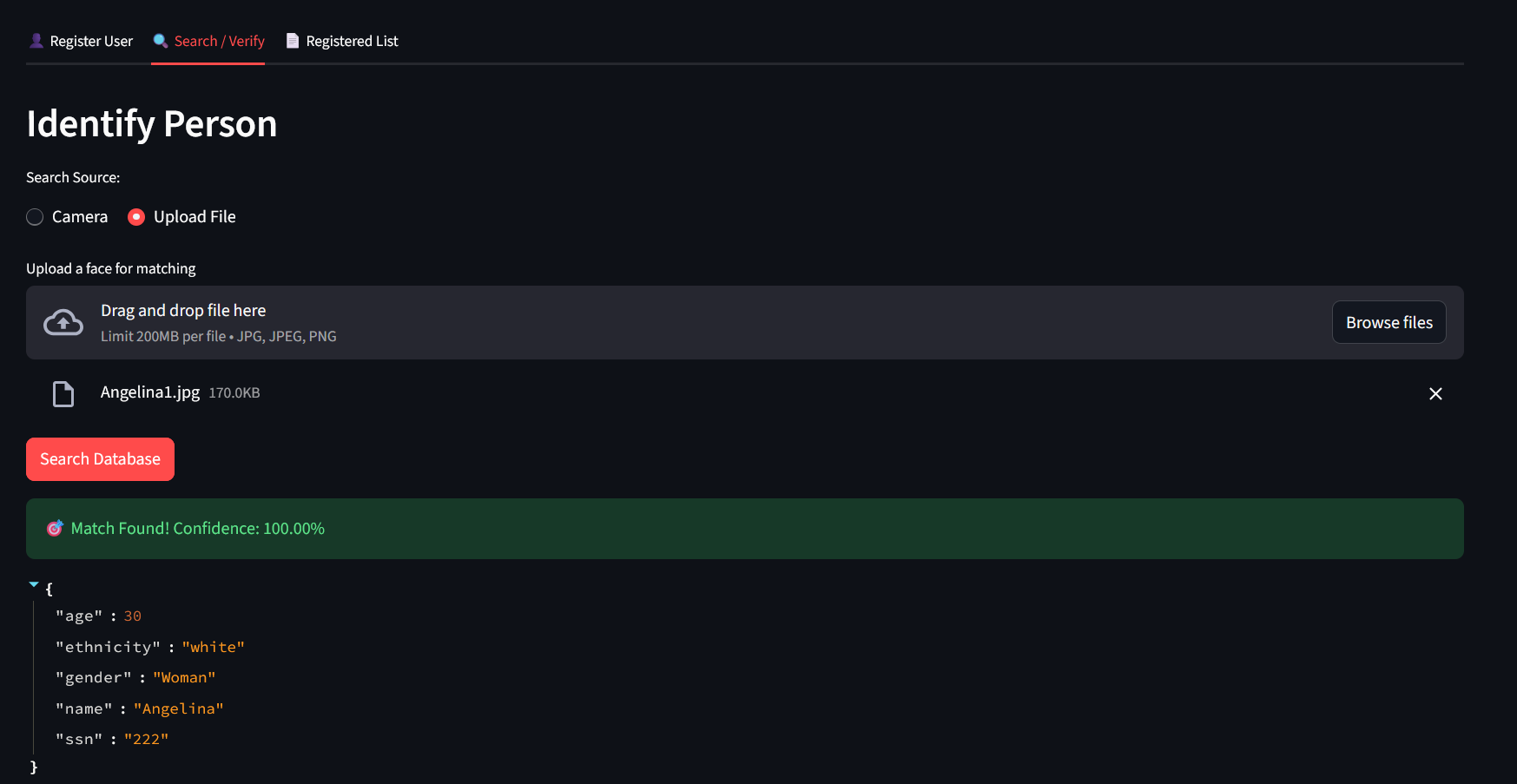
4. Find people using a photo or your camera to find people already registered (use the Search/ Verify tab):
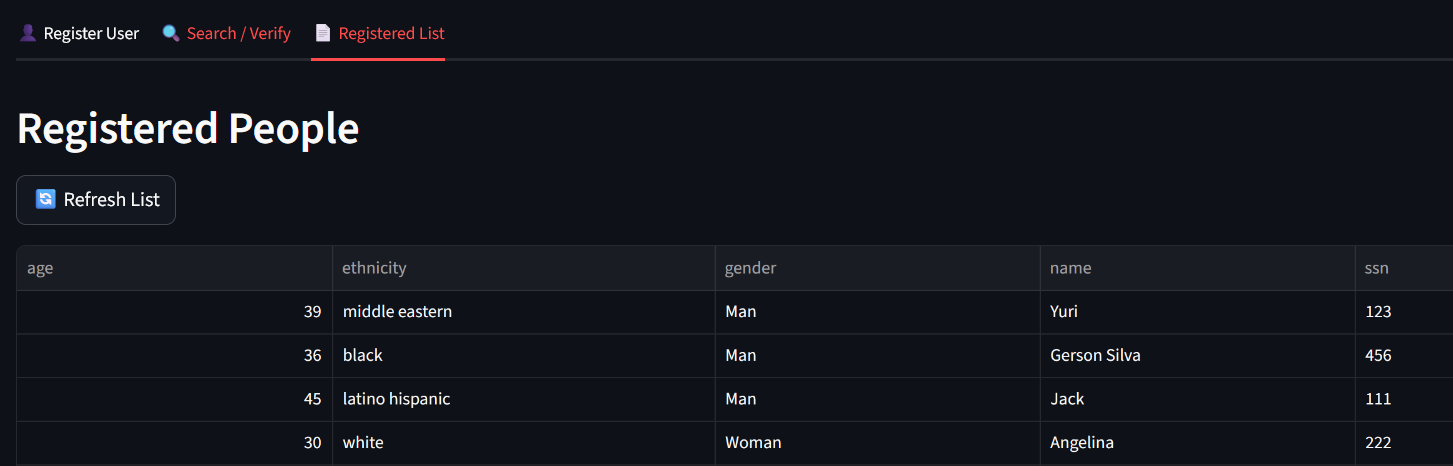
4. See all persons registered in the tab Registered List:
Details about the implementation
-
Vector Table to store embeddings:
Class dc.facialmatching.FacialData Extends (%Persistent, %JSON.Adaptor) { Property FaceVector As %Vector(%JSONINCLUDE = "none", DATATYPE = "float", LEN = 4096); Property Name As %String(MAXLEN = 100); Property Age As %Integer; Property Gender As %String; Property Ethnicity As %String; Property SSN As %String;The Property FaceVector As %Vector(%JSONINCLUDE = "none", DATATYPE = "float", LEN = 4096) allows you define the data type and length of the embedding vector. Each model can have different data types and lengths.
-
To transform and save the image as an embedded vector:
def register(): try: ssn = request.form.get('ssn') name = request.form.get('name') if 'image' not in request.files: return jsonify({"error": "Nenhum arquivo de imagem enviado"}), 400 file = request.files['image'] filestr = file.read() nparr = np.frombuffer(filestr, np.uint8) img = cv2.imdecode(nparr, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) objs = DeepFace.represent(img, model_name="VGG-Face", enforce_detection=True) embedding = objs[0]["embedding"] analysis = DeepFace.analyze(img, actions=['age', 'gender', 'race'], enforce_detection=False)[0] conn = get_iris_connection() cursor = conn.cursor() sql = """ INSERT INTO dc_facialmatching.FacialData (SSN, Name, Age, Gender, Ethnicity, FaceVector) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, TO_VECTOR(?)) """ cursor.execute(sql, ( ssn, name, int(analysis['age']), analysis['dominant_gender'], analysis['dominant_race'], json.dumps(embedding) )) conn.commit() cursor.close() conn.close()The DeepFace.represent(img, model_name="VGG-Face", enforce_detection=True) transforms face image into vector embbeding.
To insert the embbedding into IRIS uses TO_VECTOR:
INSERT INTO dc_facialmatching.FacialData (SSN, Name, Age, Gender, Ethnicity, FaceVector) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, TO_VECTOR(?)) -
To do a facial matching you must do a vectorial search:
objs = DeepFace.represent(img, model_name="VGG-Face", enforce_detection=True) current_vector = objs[0]["embedding"] conn = get_iris_connection() cursor = conn.cursor() sql = """ SELECT TOP 1 SSN, Name, Age, Gender, Ethnicity, VECTOR_DOT_PRODUCT(FaceVector, TO_VECTOR(?)) as similarity FROM dc_facialmatching.FacialData ORDER BY similarity DESC """ cursor.execute(sql, (json.dumps(current_vector),)) row = cursor.fetchone()Get the embedding using Deepface.represent and use it into the select VECTOR_DOT_PRODUCT(FaceVector, TO_VECTOR(?).
- Enjoy this solution!
Comments
Just great !
and an incredible consumption of resources on disk and cpu
with my Windows Docker Desktop
😎