Introduction to Interoperability on Python (IoP)
Interoperability on Python (IoP) is a proof-of-concept project designed to showcase the power of the InterSystems IRIS Interoperability Framework when combined with a Python-first approach.IoP leverages Embedded Python (a feature of InterSystems IRIS) to enable developers to write interoperability components in Python, which can seamlessly integrate with the robust IRIS platform. This guide has been crafted for beginners and provides a comprehensive introduction to IoP, its setup, and practical steps to create your first interoperability component. By the end of this article, you will get a clear understanding of how to use IoP to build scalable, Python-based interoperability solutions.
IoP is particularly valuable for developers working with InterSystems IRIS or IRIS for Health, since it simplifies the creation of Business Services, Business Processes, and Business Operations that use Python. Such an approach reduces the reliance on ObjectScript (the traditional language for IRIS development), making it more accessible to Python developers.
Why Should We Use IoP?
IoP offers several advantages for developers:
- Python-First Development: Python is a widely adopted, beginner-friendly language with a rich ecosystem of libraries. IoP allows developers to leverage their Python expertise within the IRIS ecosystem.
- Simplified Interoperability: IoP abstracts complex ObjectScript-based configurations, enabling faster development of interoperability components.
- Healthcare Applications: IoP is particularly suited for healthcare integrations, such as those involving FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), due to IRIS for Health's robust support for healthcare standards.
- Community and Open Source: IoP is available on PyPI and GitHub and has active community support, including contributions from developers like Guillaume Rongier (a developer evangelist for InterSystems).
Prerequisites
Before diving into IoP, ensure you have the following:
- InterSystems IRIS or IRIS for Health: A local installation or a Docker container running IRIS (Community Edition is sufficient for testing).
- Python 3.10 or later: Required for running IoP and its dependencies.
- Basic Python Knowledge: Familiarity with Python classes, functions, and package installation.
In this tutorial, we will use a local IRIS installation to create an InterSystems IRIS production featuring a Python-based Business Operation that logs a 'Hello World' message upon receiving a request. It should showcase seamless integration with the IRIS Interoperability Framework.
The following steps outline the process for achieving this goal:
- Step 1: Set Up the Virtual Environment
- Step 2: Install IoP Package
- Step 3: Set Up Environment Variables for IRIS Connection
- Step 4: Initialize the IoP Module in IRIS by using the Command line interface (CLI)
- Step 5: Create Python Business Operation: A Hello World Example
- Step 6: Migrate IoP components into IRIS
- Step 7: Production Overview
- Step 8: Test the Production Operation component
Let's begin with the step 1.
Step1: Set Up the Virtual Environment
First, set up a Python virtual environment to isolate your project’s dependencies, ensuring compatibility with IoP and InterSystems IRIS. A virtual environment is a self-contained directory with a specific Python version and the packages required for your project. Such a setup prevents conflicts with other Python projects and streamlines the development process. For this tutorial, create a folder named IOP to organize your project files.
Navigate to the IOP folder and run the following command to set up the virtual environment:
python -m venv .venv
This command creates a .venv directory in your IOP folder, containing a Python interpreter and any packages you install for your IoP project.
To activate the virtual environment on Windows, apply the next command:
.venv\Scripts\activate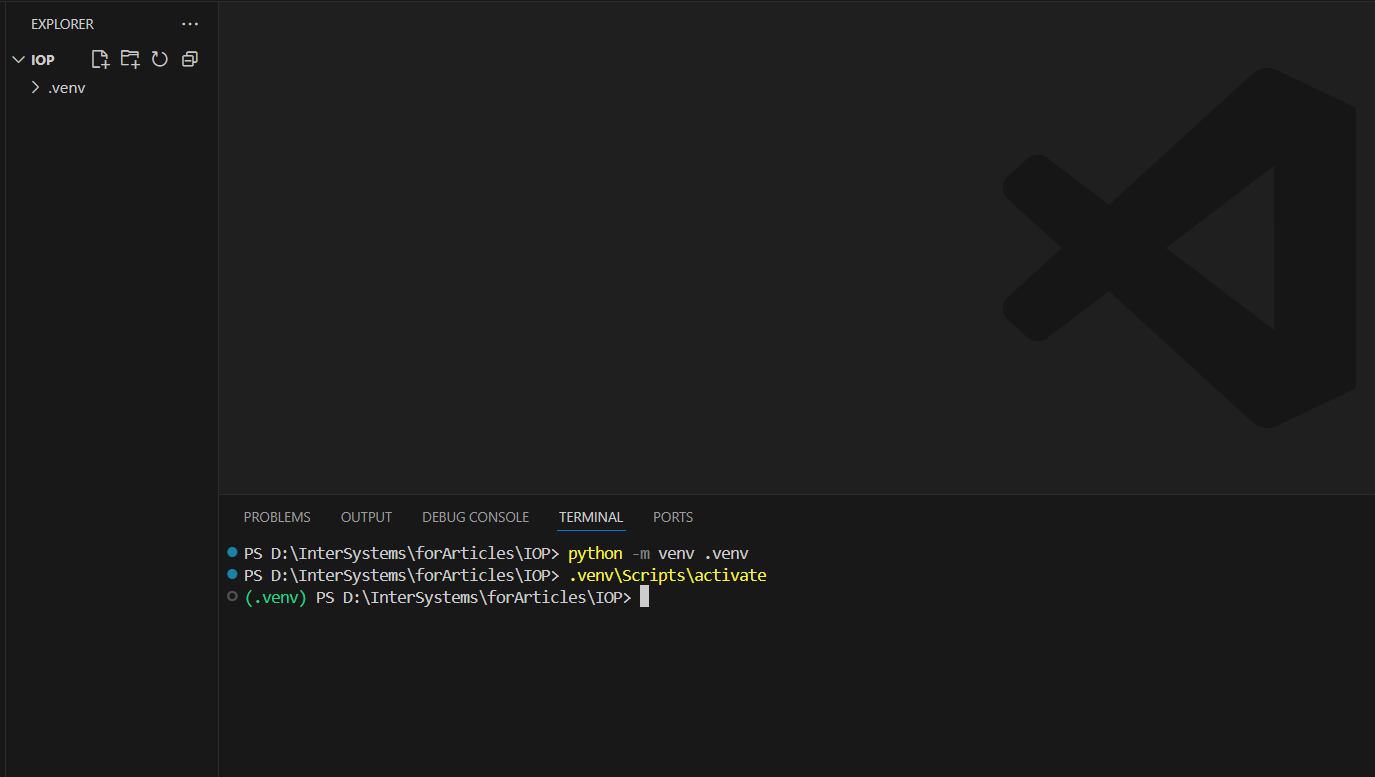
For Unix or MacOS, utilize the below command:
source .venv/bin/activate
Step 2 : Install IoP Package
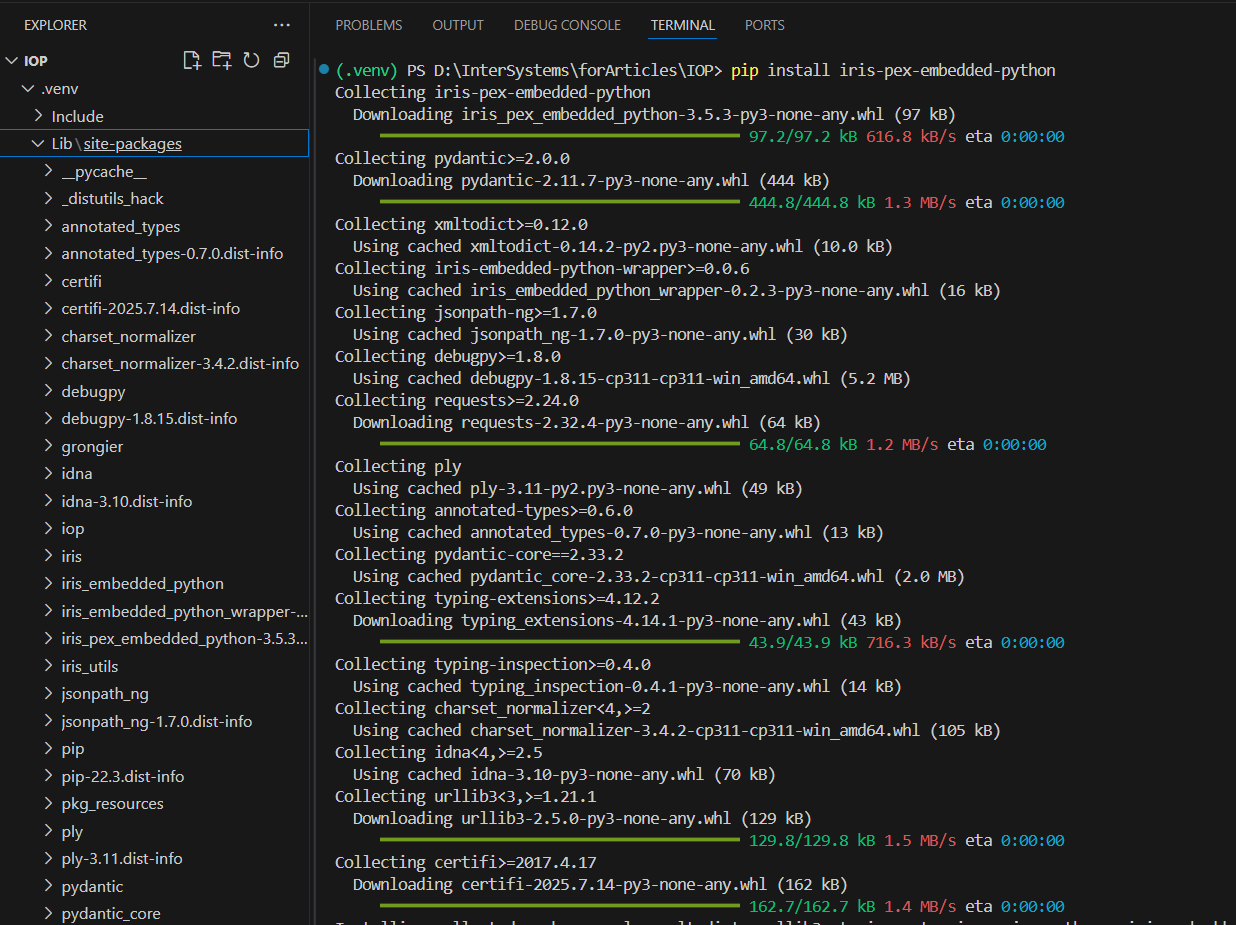
With your virtual environment activated, install the iris-pex-embedded-python package, the core dependency for your IoP project, to enable Python-based interoperability with InterSystems IRIS. Run the following command in your terminal:
pip install iris-pex-embedded-pythonThis command installs the iris-pex-embedded-python package and its dependencies from the Python Package Index (PyPI) into your virtual environment. After installation, you can use the IoP module to create Python-based interoperability components, such as the Business Operation for your IoP project.
Step 3: Set Up Environment Variables for IRIS Connection
To connect your IoP project to InterSystems IRIS, configure the environment variables specifying the connection details. For this tutorial, we will operate a local IRIS instance with an interoperability-enabled namespace named IOP:
For Windows:.png)
For Unix or MacOS:
export IRISINSTALLDIR=<installation_directory>
export IRISUSERNAME=<username>
export IRISPASSWORD=<password>
export IRISNAMESPACE=<namespace>
Step 4: Initialize the IoP Module in IRIS by using the Command line interface (CLI)
The iop command line interface (CLI) is a powerful tool for developers working with the library. In addition to --init and --migrate, it provides commands for managing your interoperability components directly from the terminal.
Some of the key commands include the following:
iop --start: Starts a production defined in yoursettings.pyfile.iop --stop: Stops a running production.iop --status: Checks the status of a production.iop --log: Views the logs from your running components.iop --init: Initialize the IoP module in irisiop --migrate: Migrate production and classes with the settings file.
Run the IoP CLI command below to initialize the IoP module in IRIS:
iop --init
This command performs the necessary configuration within your InterSystems IRIS instance, allowing it to locate and use the Python modules you create.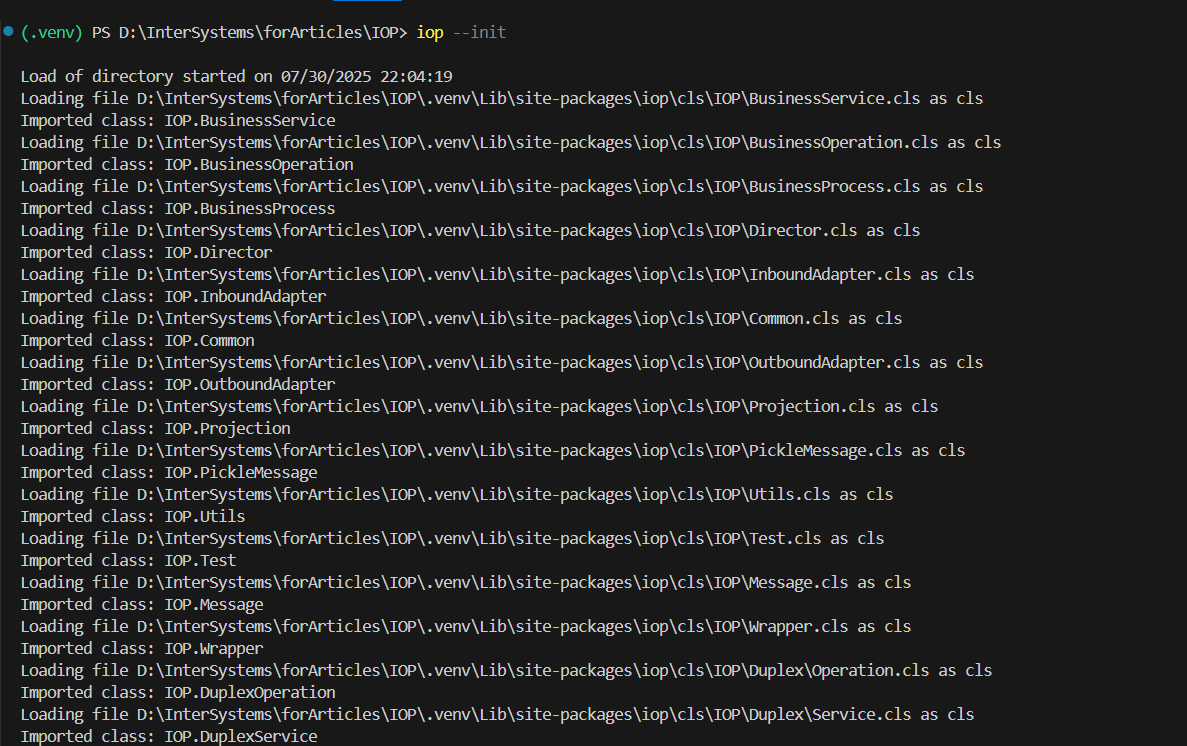
In the IRIS Management Portal, navigate to System Administration > Configuration > Classes. Select the IOP namespace, and enable the Show Generated Items check box to view the IoP-generated classes, e.g., PEX.MyBo. It will confirm that the IoP module has been successfully registered in your IRIS instance..png)
Step 5: Create Python Business Operation: A Hello World Example
Let's create a simple "Hello World" Business Operation to understand the basic structure of an IoP component.
This example will illustrate how to define a class that processes incoming messages and logs responses.
To do it, let's generate a new folder named hello_world.
mkdir hello_world
In that folder, create a new file called bo.py.
The core of your component is a Python class that inherits from BusinessOperation,which takes a message as input and returns a message as output. In between, it simply prints "Hello World" in the logs.
from iop import BusinessOperation
classMyBo(BusinessOperation):defon_message(self, request):
self.log_info("Hello World").png)
Let's explain this code.
First, we import the BusinessOperation class from the iop module.
Then, we generate a class named MyBo that inherits from BusinessOperation.
Finally, we override the on_message method. This method is called when the Business Operation receives a message.
Step 6: Migrate IoP components into IRIS
To migrate IoP components into IRIS, we need to create a new file in the hello_world folder, named settings.py.
This file contains two main settings:
CLASSES: Contains the classes used in the project.PRODUCTIONS: Includes the production name employed in the project.
from hello_world.bo import MyBo
CLASSES = {
"MyIRIS.MyBo": MyBo
}
PRODUCTIONS = [
{
'MyIRIS.Production': {
"@TestingEnabled": "true",
"Item": [
{
"@Name": "Instance.Of.MyBo",
"@ClassName": "MyIRIS.MyBo",
}
]
}
}
].png)
In this file, we import our MyBo class named MyIRIS.MyBo in IRIS, and add it to the CLASSES dictionary.
Then, we add a new production to the PRODUCTIONS list. This production will retain our MyBo class instance called Instance.Of.MyBo.
With the iop command, we can migrate the components into IRIS.
iop --migrate /path/to/hello_world/settings.py
This command will generate the production in IRIS and add the MyBo class to it..png)
Step7: Production Overview
The following production has been created by iop --migrate command: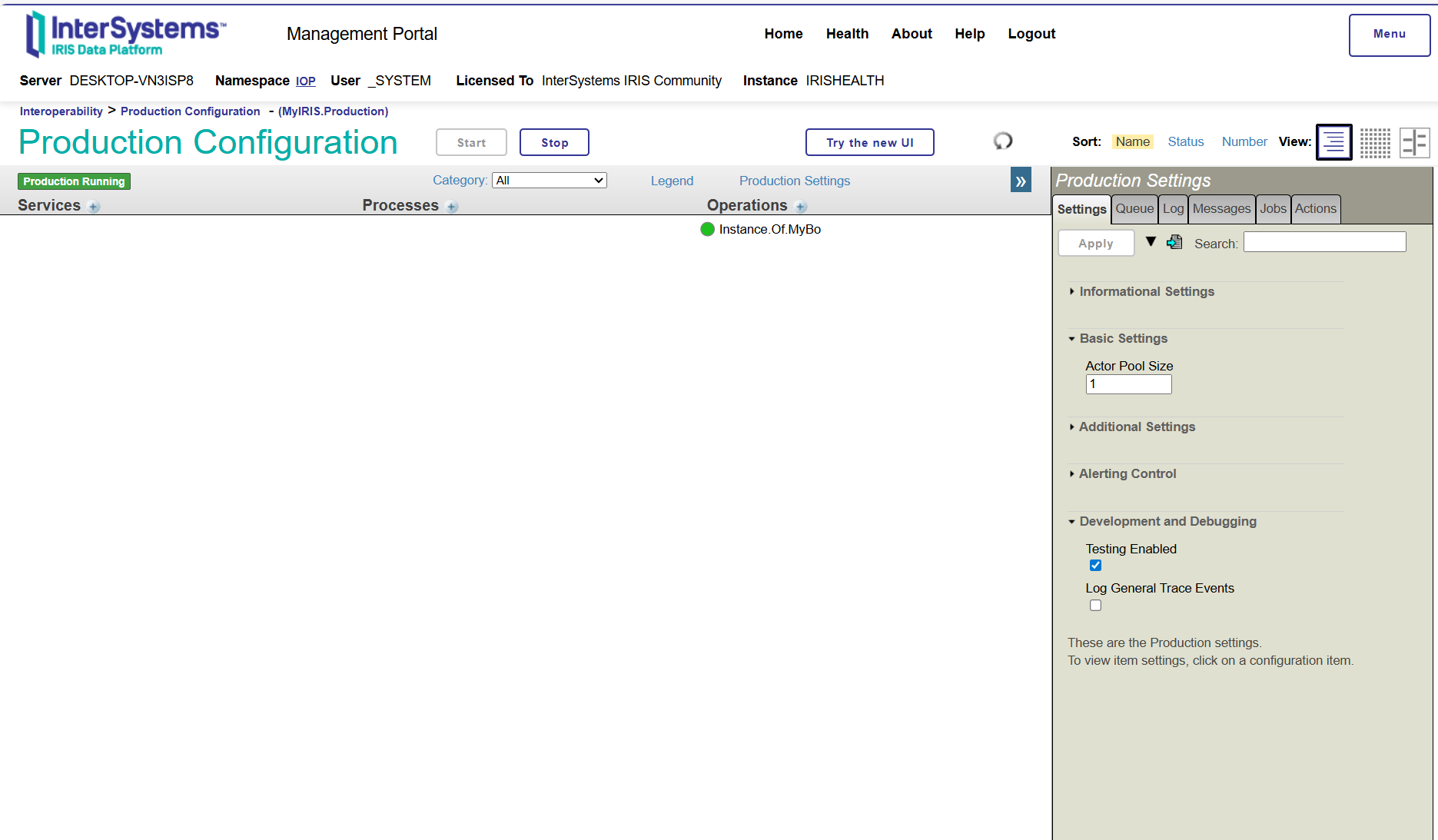
Below you can see the operation details (%classname refers to the class name in our bo.py file, %module refers to the Python file name, and %classpaths contains the path to the Python file)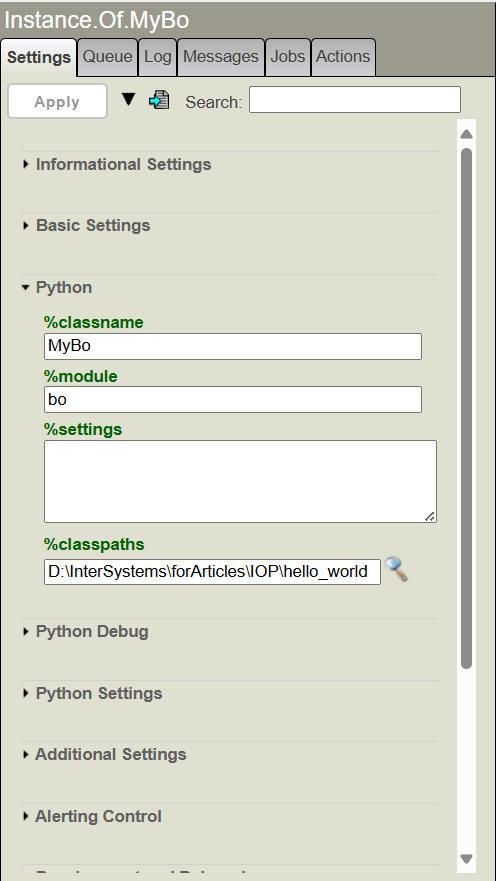
Step 8: Test the Production Operation component
To test the production, select the Business Operation. Then, go to the Actions tab and press the Test button.
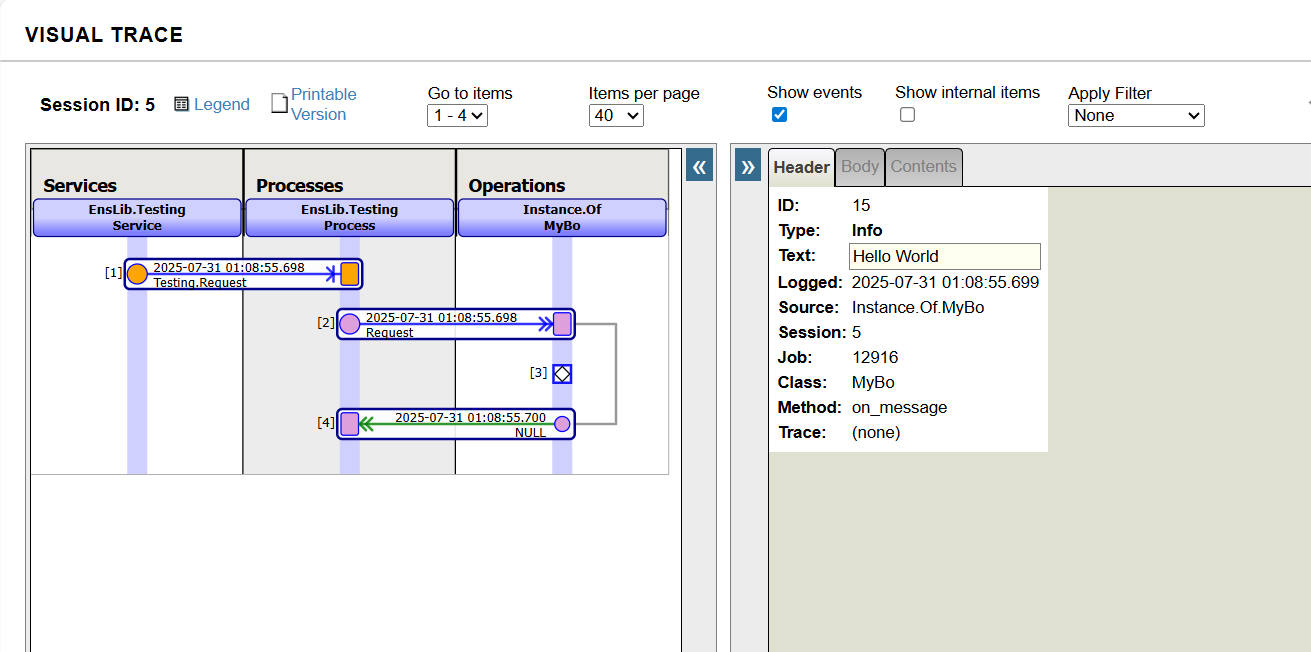
Select Ens.Request as the Request Type, click the Invoke Testing Service button, and then click Visual Trace to view the details: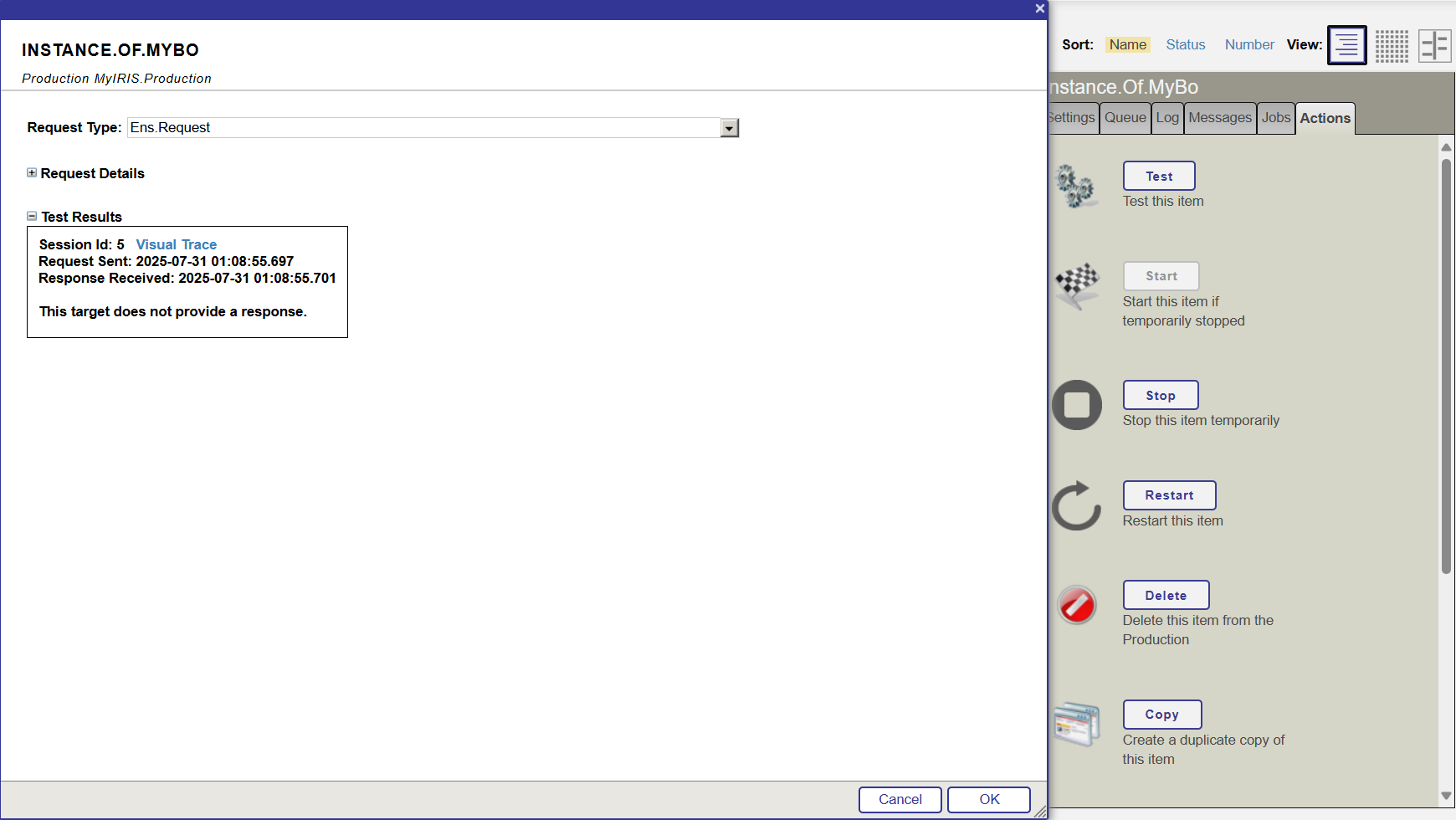
Conclusion
Interoperability on Python (IoP) opens up the InterSystems IRIS Interoperability Framework to Python developers, streamlining the process of building robust and scalable integrations. This guide has walked you through the installation of IoP, the configuration of a development environment, and the creation of a Business Operation. With IoP, you can harness the simplicity of Python alongside the power of IRIS to connect systems. For more details, view the documentation
Thanks
Comments
great article!!
Thanks @Henry Pereira
Great article! Congrats.
Thanks @André Dienes Friedrich
Great tutorial, great article congrats!!!
Thanks @Guilherme Tonelotti