
[GraphQL](http://graphql.org/) is a standard for declaring data structures and methods of data access that serves as a middleware layer between the client and the server. If you’ve never heard about GraphQL, here is a couple of useful online resources: [here](https://medium.freecodecamp.org/so-whats-this-graphql-thing-i-keep-hearing-about-baf4d36c20cf), [here](https://blog.apollographql.com/graphql-vs-rest-5d425123e34b) and [here](https://blog.apollographql.com/the-anatomy-of-a-graphql-query-6dffa9e9e747).
In this article, I will tell you how you can use GraphQL in your projects based on InterSystems technologies.
InterSystems platforms currently support several methods of creating client/server applications:
- REST
- WebSocket
- SOAP
So what’s the advantage of GraphQL? What benefits does it provide compared with REST, for example?
GraphQL has several types of requests:
- **query** - server requests for obtaining data, similar to GET requests recommended for fetching data using REST.
- **mutation** - this type is responsible for server-side data changes, similar to POST (PUT, DELETE) requests in REST.
Both mutation and query can return data – this comes in handy if you want to request updated data from the server immediately after performing a mutation.
- **subscriptions** - the same query type that will output data. The only difference is that a query is launched by a page rendered on the client side while subscriptions are activated by mutations.
## Key features and advantages of GraphQL
### It’s up to the client to decide what data should be returned
One of the key features of GraphQL is that the structure and volume of returned data are defined by the client application. The client application specifies what data it wants to receive using a declarative, graph-like structure that closely resembles the JSON format. The response structure corresponds to that of the query.
Here is how a simple GraphQL query looks:
```json
{
Sample_Company {
Name
}
}
```
A response in the JSON format:
```json
{
"data": {
"Sample_Company": [
{
"Name": "CompuSoft Associates"
},
{
"Name": "SynerTel Associates"
},
{
"Name": "RoboGlomerate Media Inc."
},
{
"Name": "QuantaTron Partners"
}
]
}
}
```
### Single endpoint
When using GraphQL to work with data, we always connect to a single **endpoint**, GQL server, and get different data by changing the structure, fields, and parameters of our queries. REST, in contrast, uses multiple endpoints.
Let’s compare REST with GraphQL using a simple example:

Let’s assume that we need to load a user’s content. If we are using REST, we need to send three queries to the server:
1. Get the user’s data by their id
2. Use their id to load their posts
3. Use their id to get a list of their followers/subscribers
Below is a REST map corresponding to these queries:
```
```
In order to get a new data set, we will need to update this REST map with a new endpoint.
GraphQL handles this with a single query. To do that, just specify the following in the request body:
```
{
operationName: null, //a query can have a name ( query TestName(...){...} )
query: "query {
User(id: "ertg439frjw") {
name
posts {
title
}
followers(last: 3) {
name
}
}
}",
variables: null // initialization of the variables used in the query
}
```
A REST map corresponding to this query:
```
```
Note that this is the only endpoint on the server.
## Installing GraphQL and GraphiQL
In order to start using GraphQL, you need to complete a few steps:
1. Download the [latest release](https://github.com/intersystems-ru/GraphQL/releases) from GitHub and import it to the necessary namespace
2. Go to the system management portal and create a new web application based on your InterSystems Data Platform product (Caché, Ensemble or IRIS):
- Name - **/**
- Namespace - **for example, SAMPLES**
- Handler class - **GraphQL.REST.Main**
3. GraphiQL — a shell for testing GraphQL queries. Download the [latest build](https://github.com/intersystems-ru/GraphQL/releases) or [build](https://github.com/graphql/graphiql) from the source on your own.
4. Create a new web application:
- Name - **/graphiql**
- Namespace - **for example, SAMPLES**
- Physical path to CSP files - **C:\InterSystems\GraphiQL\**
## Let’s take a look at the result
Go to the following link in your browser **http://localhost:57772/graphiql/index.html** (localhost — server, 57772 — port)

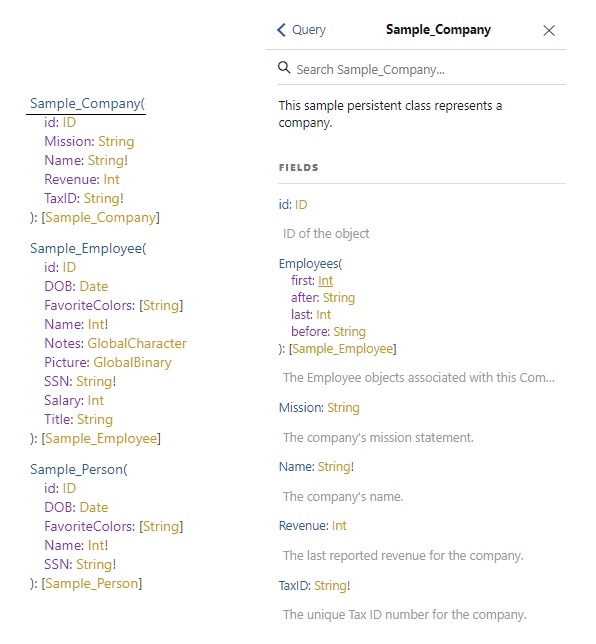
I hope everything is clear with the **Query** and **Response** namespaces. A **Schema** is a document that is generated for all stored classes in a namespace.
The schema contains:
- Classes
- Properties, arguments, and their types
- Descriptions of all of the above generated from comments
Let’s take a closer look at a schema for the **Sample_Company** class:
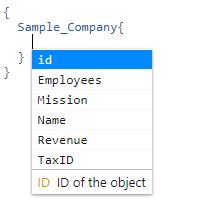
GraphiQL also supports automatic code completion that can be activated by pressing the **Ctrl + Space** key combination:
## Queries
Queries can be simple and complex for several sets of data. Below is a sample query for data from to different classes, **Sample_Person** and **Sample_Company**:

## Filtering
At the moment, only strict equality is supported:

## Pagination
Pagination is supported through 4 functions that can be combined to achieve the necessary result:
- **after: n** – all records with id greater than n
- **before: n** – all records with id smaller than n
- **first: n** – first n records
- **last: n** – last n records

## Visibility areas
In most situations, the business logic of an application dictates that particular clients only have access to particular namespace classes (role-based permissions). Based on that, you may need to limit class visibility for a client:
- All classes in the namespace (**GraphQL.Scope.All**)
- Classes inherited from a superclass (**GraphQL.Scope.Superclass**)
- Classes belonging to a particular package (**GraphQL.Scope.Package**)
In order to change the method of visibility restriction, open the studio, switch to the necessary namespace, and open the **GraphQL.Settings** class. It has a **SCOPECLASS** parameter with the default value of **GraphQL.Scope.All** — this is the class containing the description of the class visibility interface in the namespace:

To change class visibility restrictions, you need to set one of the values provided above: **GraphQL.Scope.Package** or **GraphQL.Scope.Superclass**.
If you picked **GraphQL.Scope.Package**, you will also need to go to that class and change the value of the **Package** parameter to the name of the necessary package – for instance, **Sample**. This will make all the stored classes from this package fully available:

If you picked **GraphQL.Scope.Superclass**, simply inherit from this class once again in the necessary classes::

## Currently supported
Queries:
- Basic
- Embedded objects
- Only many to one relation
- List of simple types
- List of objects
## Currently under development
Queries:
- Embedded objects
- Support of relations of all types
- Filtering
- Support of inequalities
## Plans
- Mutaions
- [Aliases](https://graphql.github.io/learn/queries/#aliases)
- [Directives](https://graphql.github.io/learn/queries/#directives)
- [Fragments ](https://graphql.github.io/learn/queries/#fragments)
→ [Link ](https://github.com/intersystems-community/GraphQL) to the project repository
→ [Link ](http://37.139.6.217:57773/graphiql/index.html) to the demo server
Issues Pull Requests are very welcome.
Keep an eye on our project updates!